Introduction
Web scraping has become a crucial technique for extracting valuable insights from the extensive array of online information. The market for web data collection is projected to reach $6.2 billion by 2026. This tutorial outlines the essential steps for mastering Python web scraping, equipping readers with the necessary tools and knowledge to effectively utilise this powerful method for data extraction and analysis.
However, as the demand for web scraping increases, so do the ethical and legal considerations that accompany it. How can one navigate these complexities while efficiently gathering data?
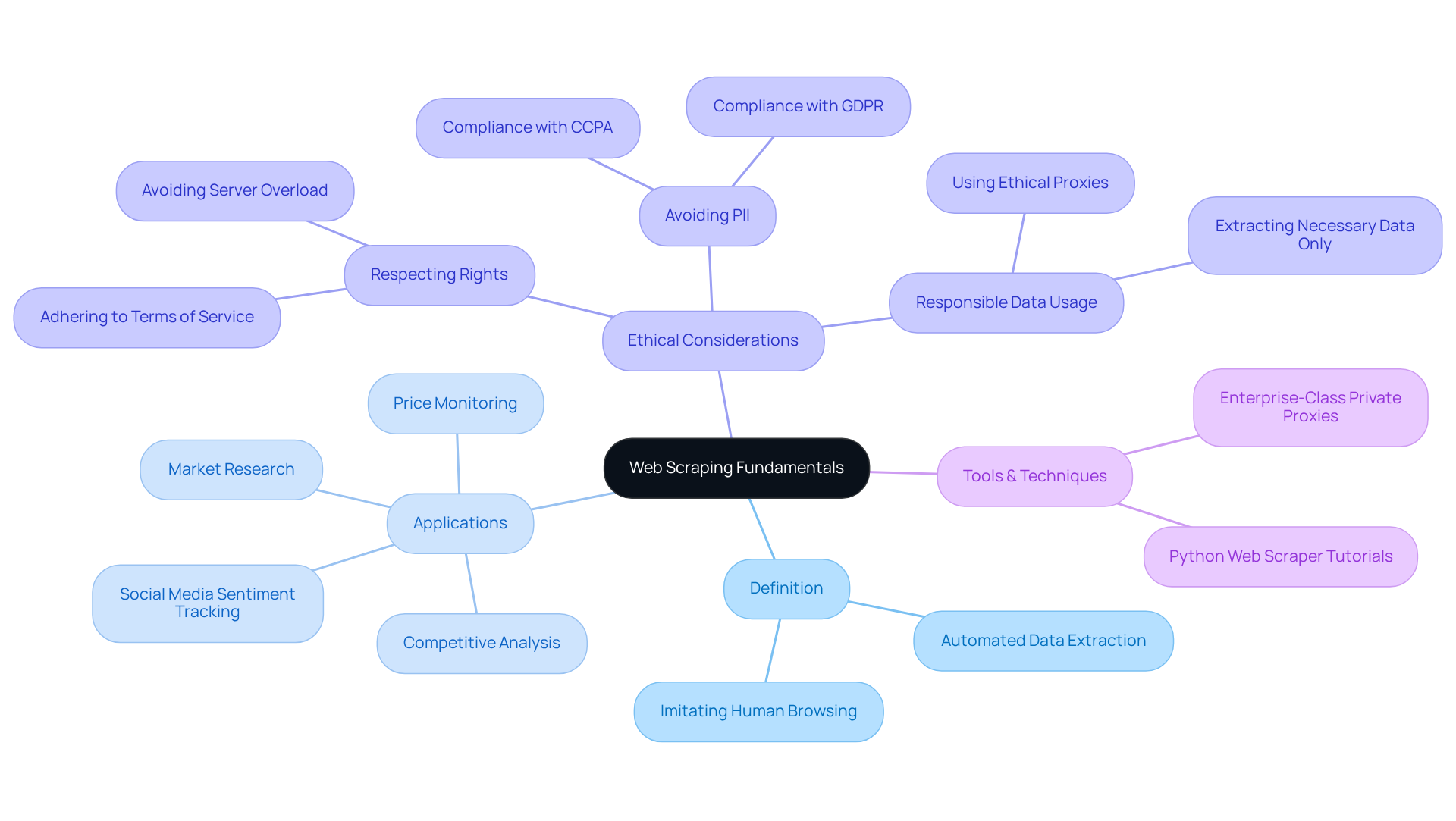
Understand the Fundamentals of Web Scraping
Web harvesting is the automated method of extracting information from websites, utilising bots or scripts to collect content that can be structured and analysed. This technique has experienced considerable growth, with the web data collection market anticipated to reach $6.2 billion by 2026, indicating its rising significance in various sectors.
Definition: Web harvesting entails retrieving information from web pages using tools or scripts that imitate human browsing behaviour. This allows for efficient data collection and analysis.
Applications: The uses of web data extraction in digital marketing are extensive, including:
- Market research
- Price monitoring
- Competitive analysis
- Social media sentiment tracking
Businesses leverage these insights to make informed decisions and enhance their strategies.
Ethical Considerations: Ethical web data extraction is paramount. It is essential to examine a website's robots.txt file to comprehend its data collection policies and ensure adherence to legal standards, such as GDPR and CCPA. Ethical practises include:
- Respecting website owners' rights
- Avoiding the collection of personally identifiable information (PII)
- Adhering to terms of service
Recent case studies highlight the significance of ethical proxies and responsible information usage, emphasising that scrapers should only extract necessary information to avoid legal repercussions.
To enhance the effectiveness of web data extraction, especially in the realms of SEO and digital marketing, utilising enterprise-class private proxy servers, such as those offered by Trusted Proxies, is crucial. These proxies not only offer a secure and dependable infrastructure but also enhance the speed and effectiveness of information extraction processes, ensuring adherence to industry standards. Grasping these basics is crucial for anyone aiming to efficiently employ a python web scraper tutorial in their projects, ensuring that they manage the intricacies of information gathering responsibly.
Set Up Your Python Environment and Tools
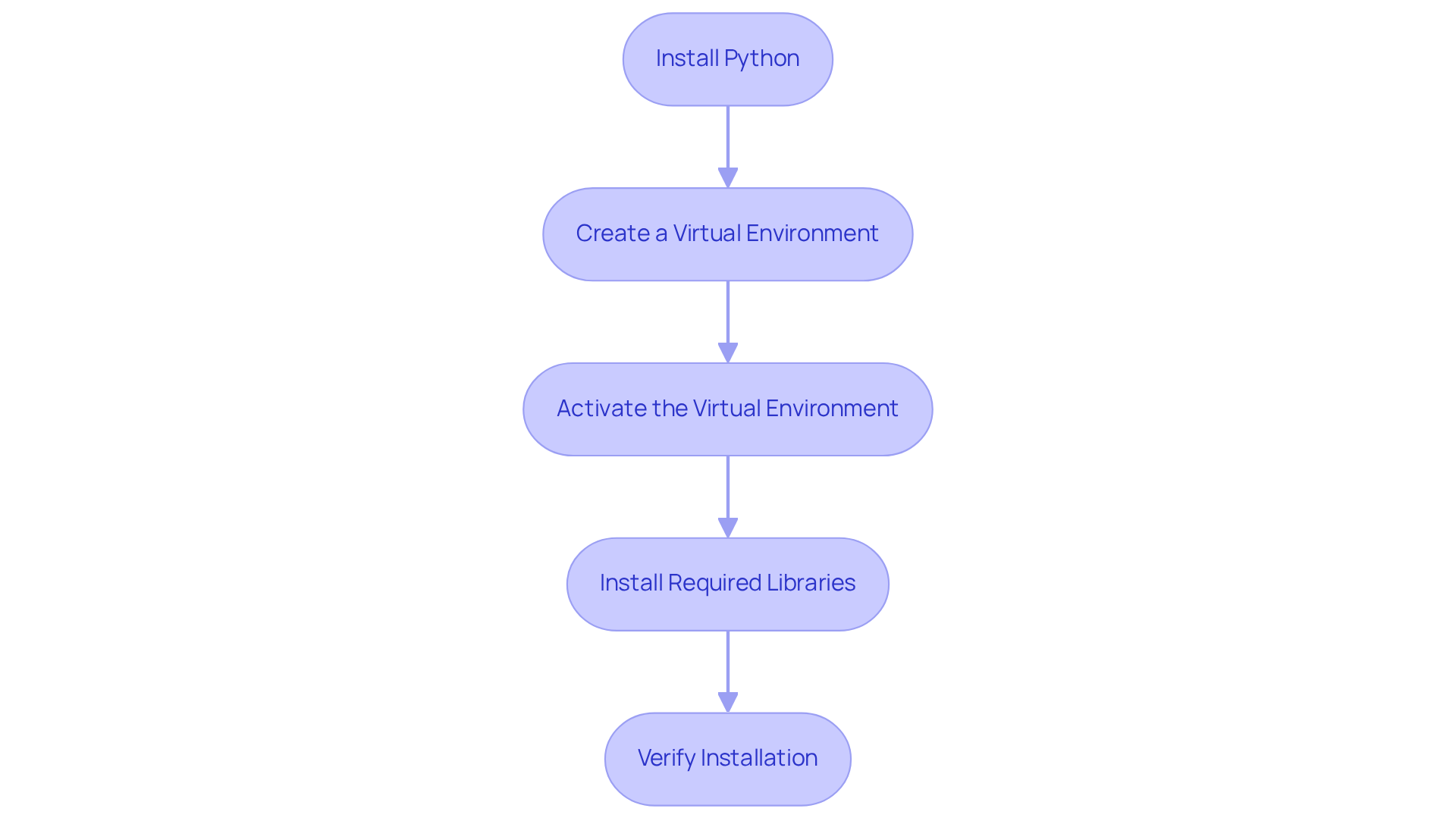
To begin web scraping with Python using Appstractor's efficient data extraction solutions, follow these steps:
- Install Python: Download and install the latest version of Python from the official website.
- Create a Virtual Environment: Use the command
python -m venv myenvto create an isolated environment for your project. - Activate the Virtual Environment: On Windows, use
myenv\Scripts\activate, and on macOS/Linux, usesource myenv/bin/activate. - Install Required Libraries: Use pip to install essential libraries:
pip install requestsfor making HTTP requests.pip install beautifulsoup4for parsing HTML.pip install pandasfor data manipulation.
- Verify Installation: Run a simple script to ensure all libraries are correctly installed and functioning.
Additionally, utilising Appstractor's rotating proxy servers can enhance your web extraction efforts by providing self-serve IPs that help evade IP bans. Their full-service options also offer ready-to-use information delivery for more complex projects. This setup provides a robust foundation for executing web scraping tasks effectively, making it a valuable resource in any python web scraper tutorial, ensuring efficient information extraction and seamless integration with your existing workflows.
Execute Data Extraction with Python: Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively execute data extraction using Python, follow these detailed steps:
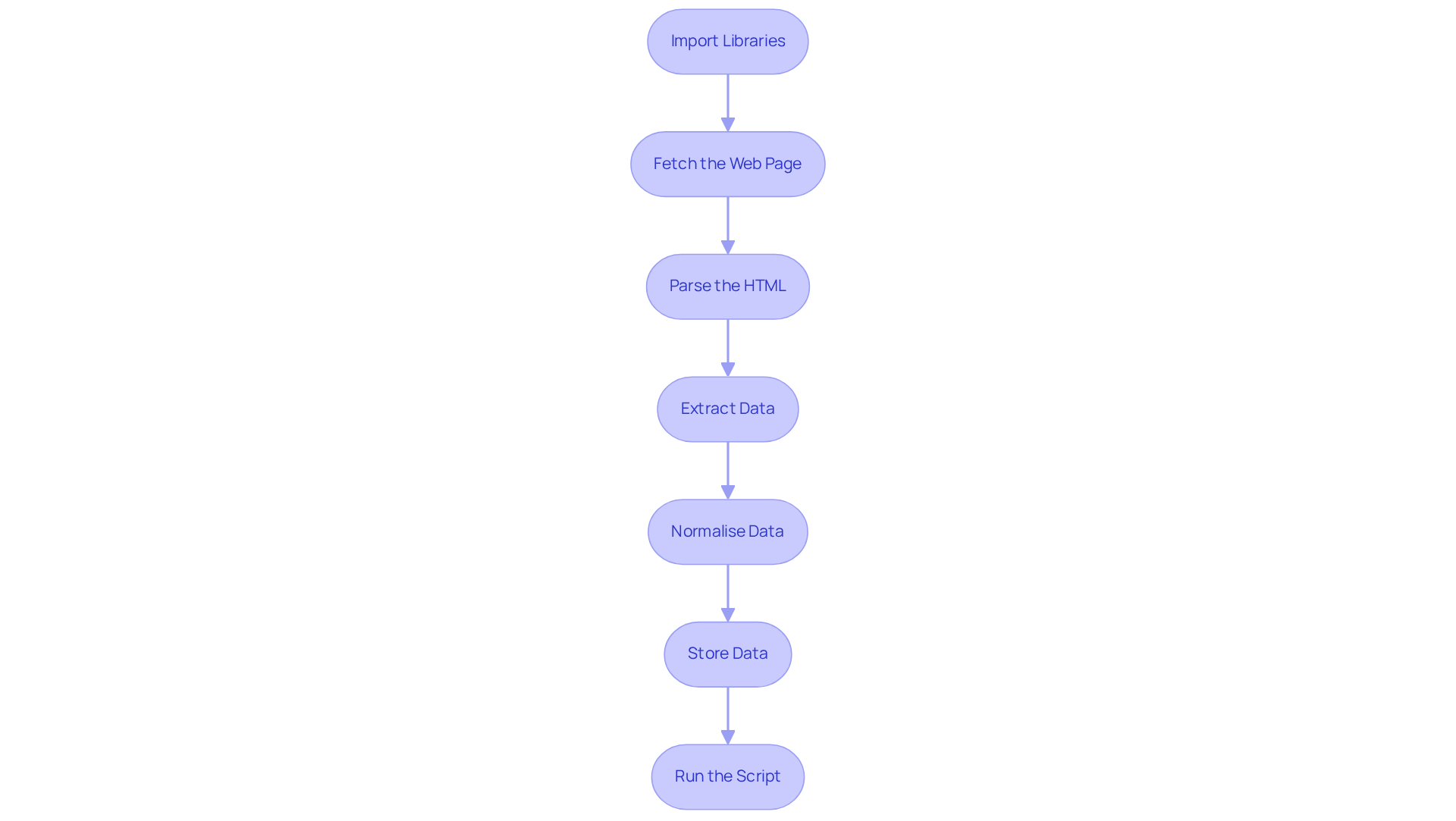
-
Import Libraries: Begin by importing the essential libraries for your script:
import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup import pandas as pd -
Fetch the Web Page: Utilise the requests library to retrieve the HTML content of your target page:
url = 'https://example.com' response = requests.get(url) html_content = response.text -
Parse the HTML: Create a BeautifulSoup object to parse the HTML content:
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, 'html.parser') -
Extract Data: Identify the specific HTML elements that contain the data you need and extract it:
data = soup.find_all('div', class_='data-class') extracted_data = [item.text for item in data] -
Normalise Data: Clean the extracted text and convert dates into standard formats to ensure data quality:
# Example of normalising data normalized_data = [normalize_text(item) for item in extracted_data] -
Store Data: Convert the extracted data into a DataFrame for easier manipulation and analysis:
df = pd.DataFrame(normalized_data, columns=['Data']) -
Run the Script: Execute your script to view the results. Be prepared to adjust the selectors based on the website's structure, as major news portals often update their layouts every 3-6 months. To enhance your information extraction capabilities, consider utilising Appstractor's rotating proxy servers, which can help maintain anonymity and prevent IP bans during your harvesting activities. Furthermore, if you require a more comprehensive solution, Appstractor offers full-service options that can manage information extraction seamlessly, allowing you to focus on analysis rather than the technical aspects of collection. Remember to comply with legal and ethical standards when gathering information, and consider adopting a 'stealth-first' approach to mimic human behaviour and avoid IP bans.
This python web scraper tutorial provides you with the essential tools to carry out your own extraction tasks effectively, leveraging Python's powerful libraries. As you refine your skills, keep in mind that effective information extraction relies on understanding the webpage structure and adapting your approach accordingly. As Joo Ann Lee aptly stated, "Information science isn't about the quantity of information but rather the quality.
Manage and Export Your Scraped Data Effectively
Once you have gathered your information, effective management and exportation are crucial for analysis. Here’s how to do it:
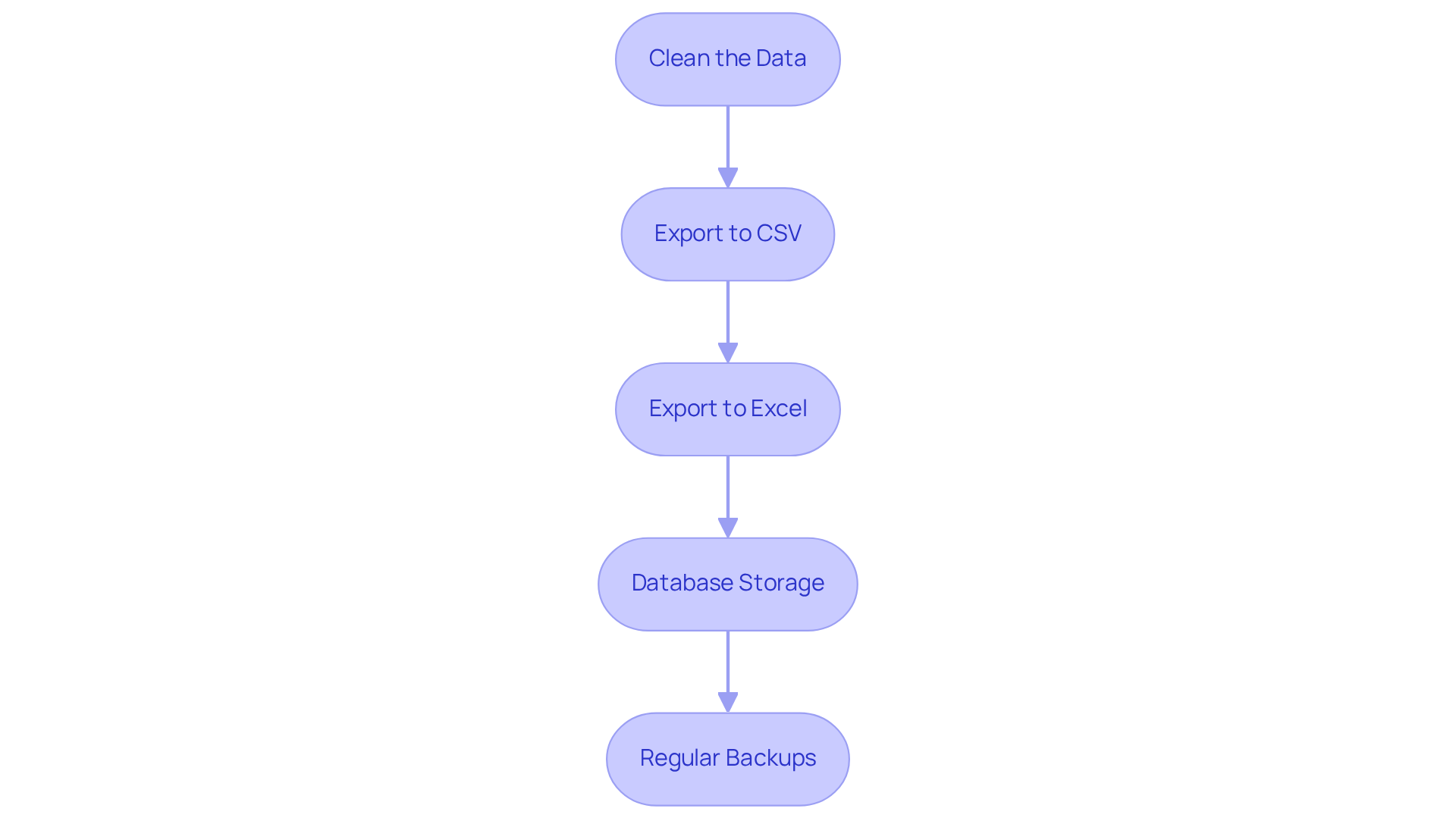
-
Clean the Data: Utilise Pandas to refine your DataFrame by eliminating duplicates and addressing missing values:
df.drop_duplicates(inplace=True) df.fillna('', inplace=True)Data analysts emphasise that prioritising efficient data cleaning techniques is essential, as nearly 47% of newly created records contain at least one critical error. Furthermore, automated validation at ingestion can prevent costly late fixes, underscoring the significance of comprehensive information cleaning.
-
Export to CSV: Save your cleaned data to a CSV file for straightforward access:
df.to_csv('scraped_data.csv', index=False)This format is widely used for its simplicity and compatibility with various data analysis tools.
-
Export to Excel: For more intricate data analysis, export to Excel:
df.to_excel('scraped_data.xlsx', index=False)Excel allows for advanced functionalities, making it a preferred choice for many analysts. To manage Excel files in Python, you can instal libraries such as Pandas using the command
pip instal pandas. -
Database Storage: For larger datasets, consider placing your information in a database. Use SQLAlchemy to connect to a database and store your DataFrame:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine engine = create_engine('sqlite:///scraped_data.db') df.to_sql('data_table', con=engine, if_exists='replace', index=False)This method enhances data integrity and accessibility, especially for ongoing projects.
-
Regular Backups: Establish a backup approach to prevent information loss, ensuring that your scraped content is secure and recoverable. Ongoing observation and verification of your datasets are essential, as information quality can diminish over time. Organisations can lose over $5 million yearly due to inadequate management practises. Continuous profiling, verification, and enrichment are necessary to maintain the accuracy of information.
By following the guidelines in the python web scraper tutorial, you can ensure that your scraped data is well-managed and primed for insightful analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, web scraping has become an essential tool for extracting valuable information from websites, allowing businesses to leverage data for informed decision-making. A solid understanding of its fundamentals, including ethical considerations and technical setup, is crucial for anyone aiming to utilise Python for effective web scraping. This tutorial has provided a comprehensive guide, outlining the necessary steps to establish a Python environment, execute data extraction, and manage the resulting data efficiently.
Key insights include:
- The importance of respecting website policies.
- The use of essential libraries such as Requests and BeautifulSoup.
- The significance of data cleaning and storage.
By adhering to these outlined steps, individuals can not only gather data but also ensure its quality and accessibility, which are vital for meaningful analysis. The tutorial underscores that web scraping is not solely about quantity; it is about extracting quality information that can drive strategic insights.
As web scraping continues to evolve, it is paramount to stay informed about best practises and ethical standards. Embracing these principles enhances the effectiveness of data extraction and fosters responsible usage of information. By implementing the strategies discussed, individuals and organisations can leverage Python web scraping to unlock new opportunities and insights, ultimately transforming data into a powerful asset for growth and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping?
Web scraping, also known as web harvesting, is the automated method of extracting information from websites using bots or scripts that imitate human browsing behaviour, allowing for efficient data collection and analysis.
What is the projected growth of the web data collection market?
The web data collection market is anticipated to reach $6.2 billion by 2026, indicating its rising significance across various sectors.
What are some common applications of web data extraction in digital marketing?
Common applications include market research, price monitoring, competitive analysis, and social media sentiment tracking, which help businesses make informed decisions and enhance their strategies.
Why are ethical considerations important in web scraping?
Ethical considerations are paramount to ensure compliance with legal standards, respect website owners' rights, and avoid collecting personally identifiable information (PII). Adhering to terms of service is also crucial.
What practises should be followed for ethical web data extraction?
Ethical practises include examining a website's robots.txt file, respecting website owners' rights, avoiding the collection of PII, and adhering to legal standards such as GDPR and CCPA.
How can the use of proxies enhance web data extraction?
Utilizing enterprise-class private proxy servers, such as those offered by Trusted Proxies, enhances the speed and effectiveness of information extraction processes while ensuring adherence to industry standards.
What should one understand before using a Python web scraper?
It is crucial to grasp the fundamentals of web scraping, including ethical practises and the use of reliable proxies, to manage the intricacies of information gathering responsibly.
List of Sources
- Understand the Fundamentals of Web Scraping
- Thundergits Technologies - Innovative Tech Solutions (https://thundergits.com/blogs/the-ethical-web-scraping.html)
- Ethical and Legal Considerations When Web Scraping Public Data. Learn how Techno Softwares ensures compliance while delivering powerful data solutions. (https://technosoftwares.com/blog/ethical-and-legal-considerations-when-web-scraping-public-data)
- The Complete Guide to Ethical Web Scraping (https://rayobyte.com/blog/ethical-web-scraping)
- Ethics in Web Scraping (https://medium.com/data-science/ethics-in-web-scraping-b96b18136f01)
- Set Up Your Python Environment and Tools
- Best Python Web Scraping Tools 2026 (Updated) (https://medium.com/@inprogrammer/best-python-web-scraping-tools-2026-updated-87ef4a0b21ff)
- Web Scraping News Articles with Python (2026 Guide) (https://capsolver.com/blog/web-scraping/web-scraping-news)
- Web Scraping for News Articles using Python– Best Way In 2026 (https://proxyscrape.com/blog/web-scraping-for-news-articles-using-python)
- Scraping ‘Quotes to Scrape’ website using Python (https://medium.com/@kshamasinghal/scraping-quotes-to-scrape-website-using-python-c8a616b244e7)
- Execute Data Extraction with Python: Step-by-Step Guide
- 20 Data Science Quotes by Industry Experts (https://coresignal.com/blog/data-science-quotes)
- Web Scraping for News Articles using Python– Best Way In 2026 (https://proxyscrape.com/blog/web-scraping-for-news-articles-using-python)
- Scraping Google News: The 2026 Python Guide | HasData (https://hasdata.com/blog/web-scraping-google-news)
- Web Scraping News Articles with Python (2026 Guide) (https://capsolver.com/blog/web-scraping/web-scraping-news)
- Scrape TechCrunch News with Python - Complete Guide (https://webparsers.com/how-to-scrape-techcrunch-news-with-python-step-by-step-guide)
- Manage and Export Your Scraped Data Effectively
- Python Export to Excel (Developer Tutorial) (https://ironsoftware.com/python/excel/blog/using-ironxl-for-python/python-export-to-excel-tutorial)
- File Data Preparation Efficiency Stats — 38 Critical Statistics Every Data Leader Should Know in 20 (https://integrate.io/blog/file-data-preparation-efficiency-stats)
- Scraping Google news using Python (2026 Tutorial) (https://serpapi.com/blog/scraping-google-news-using-python-tutorial)
- Data cleaning techniques: methods, steps, and best practices (2026) (https://ovaledge.com/blog/data-cleaning-techniques)




