Introduction
Web scraping has become a crucial technique for businesses aiming to leverage the vast amount of information available online. By automating data extraction from websites, organisations can gain essential insights that inform strategic decisions and improve their competitive edge. However, as the web scraping landscape evolves, so do the challenges and ethical considerations that accompany it.
How can businesses effectively navigate these complexities while mastering web scraping with Python? This guide explores the fundamental steps, tools, and best practises to empower readers in building their own web scrapers. By following these guidelines, businesses can ensure compliance and efficiency in an increasingly data-driven environment.
Understand Web Scraping and Its Importance
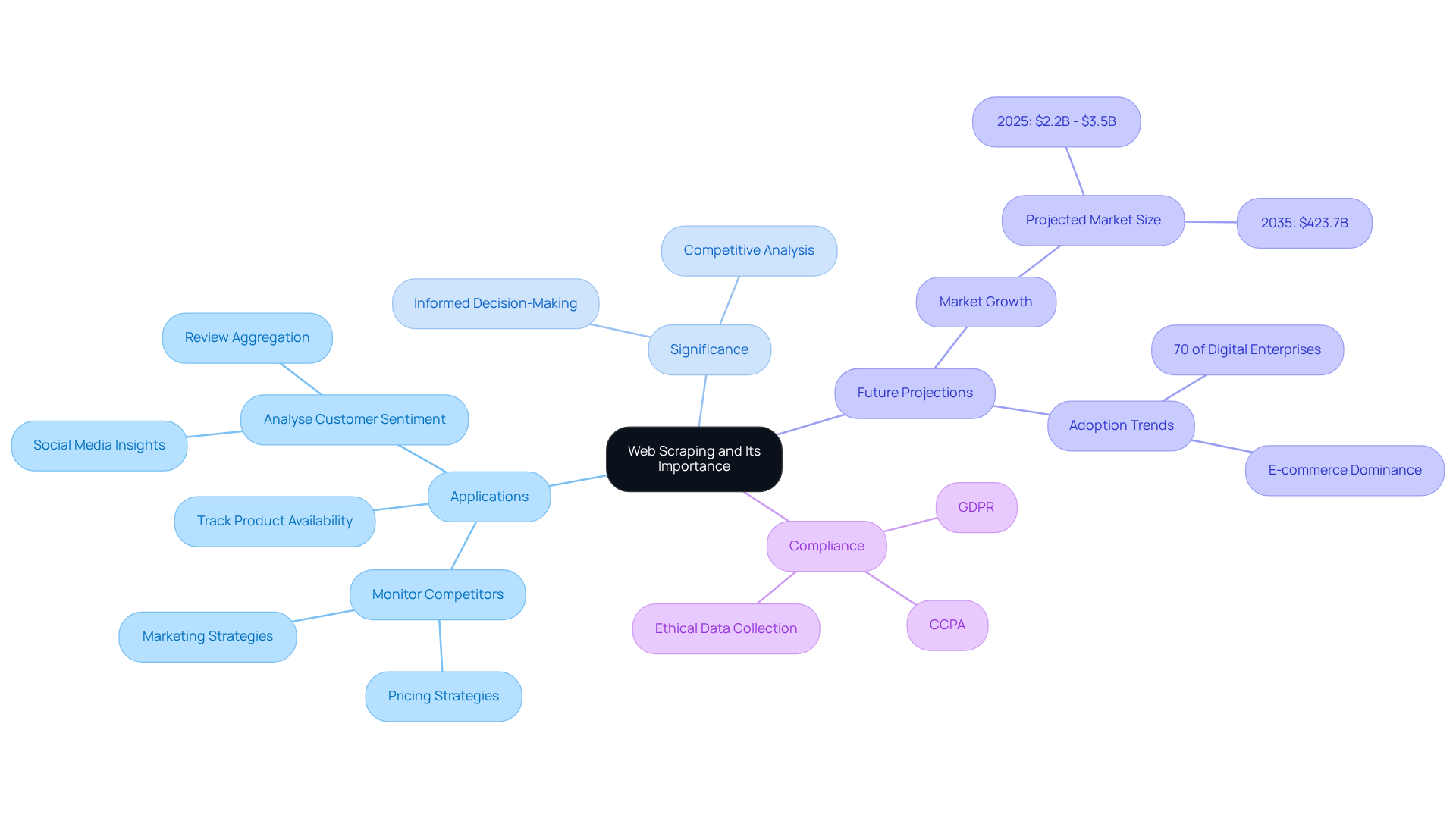
Web harvesting, or how to do web scraping using Python, serves as an automated method for extracting information from websites, enabling companies to gather extensive insights swiftly and effectively. Its significance lies in the insights it provides, which can drive informed decision-making, enhance competitive analysis, and support comprehensive market research.
For instance, companies utilise web data extraction to:
- Monitor competitors' pricing strategies
- Track product availability
- Analyse customer sentiment through social media platforms
By 2025, over 70% of digital enterprises are expected to leverage publicly accessible data for market intelligence, underscoring the growing reliance on web extraction tools.
Moreover, a mid-sized e-commerce retailer reported a remarkable 300% increase in ROI on promotional campaigns after implementing a custom data extraction system that monitored competitor websites every 15 minutes. This illustrates how mastering techniques on how to do web scraping using Python can empower businesses to stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Testimonials from users of Trusted Proxies highlight the substantial impact of proxy services on SEO effectiveness and data precision, both of which are crucial for efficient web extraction. For example, a CEO remarked that combining Trusted Proxies with tools like Google Search Console facilitated deep monitoring and ranking insights, contributing to larger SEO projects. Another user, a Freelance SEO Consultant, noted that their reports ran four times faster and were more accurate since adopting Trusted Proxies. Such experiences underscore the importance of reliable proxies in enhancing web data collection efforts.
Additionally, it is vital for businesses to comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to ensure ethical data collection practices. The web data extraction market is projected to experience significant growth, reaching between $2.2 billion and $3.5 billion by 2025, further emphasising its increasing importance in business strategies.
Set Up Your Python Environment and Tools
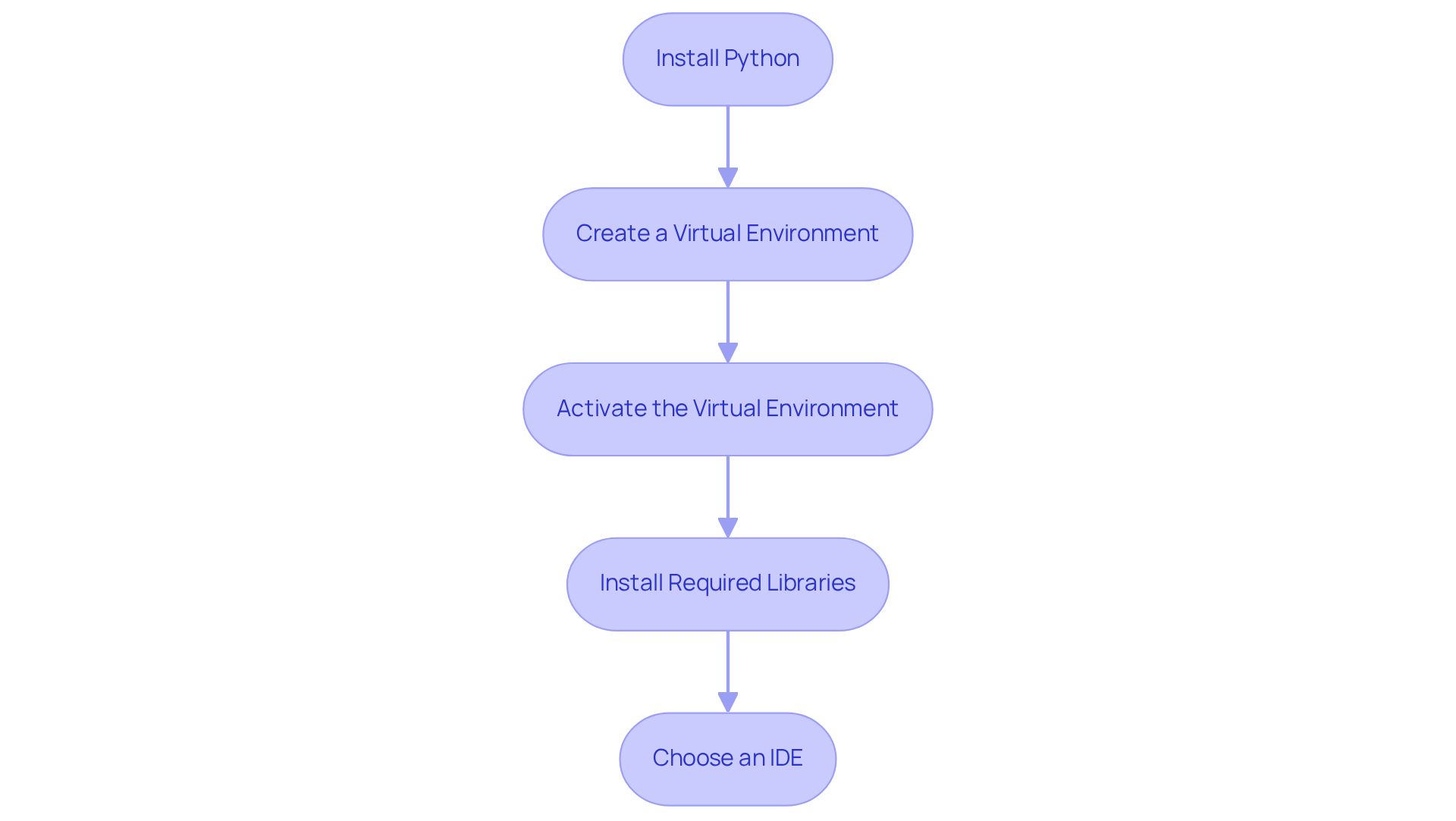
To effectively start web scraping with Python, follow these essential steps to set up your environment:
-
Install Python: Download the latest version of Python (3.11+) from the official website. Ensure you check the box to add Python to your PATH during installation.
-
Create a Virtual Environment: Open your command line interface (CLI) and create a virtual environment to manage dependencies with the command:
python -m venv myenv -
Activate the Virtual Environment: Activate your virtual environment using the following commands:
- On Windows:
myenv\Scripts\activate - On macOS/Linux:
source myenv/bin/activate
- On Windows:
-
Install Required Libraries: Install essential libraries for web scraping, such as Requests and BeautifulSoup, using pip:
pip install requests beautifulsoup4Notably, BeautifulSoup is utilised by 43.5% of developers for HTML/XML parsing, making it a popular choice in the web scraping community.
-
Choose an IDE: Select an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like PyCharm or Visual Studio Code to write your scripts. This choice enhances your coding experience with features like syntax highlighting and debugging tools.
By following these steps, you will learn how to do web scraping using Python to create a fully operational Python environment designed for web extraction, allowing you to efficiently retrieve and analyse information. Furthermore, consider utilising Appstractor's advanced information mining solutions, which provide automated web information extraction with flexible proxy options, including rotating proxies and comprehensive services. This integration can significantly enhance your data collection capabilities while ensuring compliance with local regulations and terms of service.
Build Your Web Scraper: Step-by-Step Instructions
To build your web scraper, follow these detailed steps:
-
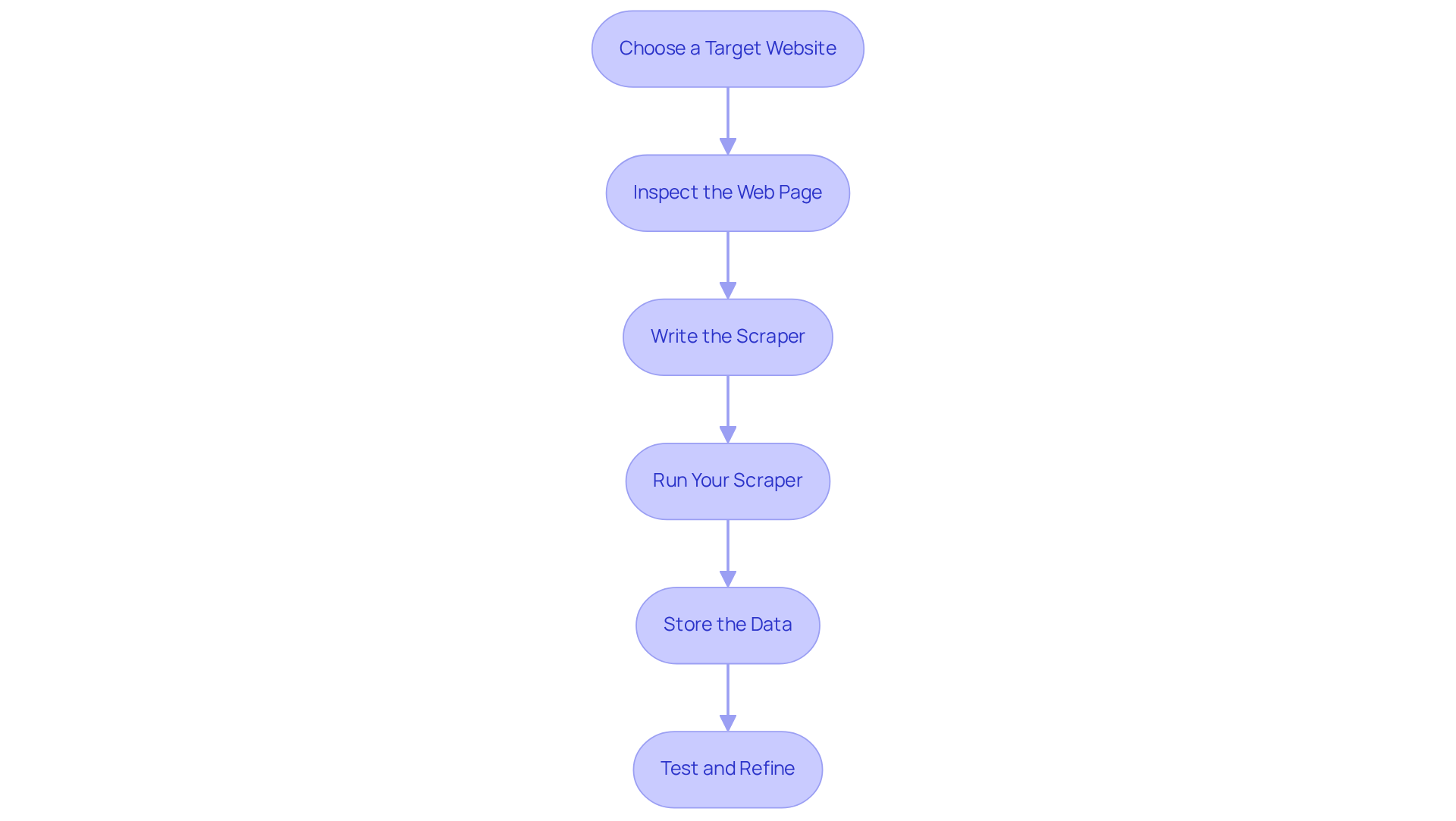
Choose a Target Website: Identify a website from which you wish to extract information. Before proceeding, review the site's terms of service to ensure that scraping is permitted.
-
Inspect the Web Page: Utilise your browser's developer tools (right-click on the page and select 'Inspect') to examine the HTML structure. Concentrate on recognising the particular elements that hold the information you plan to extract.
-
Write the Scraper: Create a new Python file (e.g.,
scraper.py) and begin coding:import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup url = 'https://example.com' response = requests.get(url) soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser') # Extract data data = soup.find_all('div', class_='data-class') for item in data: print(item.text) -
Run Your Scraper: Execute your script in the terminal with the following command:
python scraper.py -
Store the Data: Enhance your script to save the extracted data into a CSV file:
import csv with open('data.csv', 'w', newline='') as csvfile: writer = csv.writer(csvfile) writer.writerow(['Header1', 'Header2']) # Add headers for item in data: writer.writerow([item.text]) -
Test and Refine: Run your updated script and verify the contents of the
data.csvfile for the extracted information. Make necessary adjustments to your code to enhance accuracy and efficiency.
By following these steps, you will successfully understand how to do web scraping using python to create a functional web scraper capable of extracting data from your chosen online source.
Troubleshoot Common Web Scraping Issues
As you embark on learning how to do web scraping using python, you may encounter several common issues. Below are solutions to address these challenges:
-
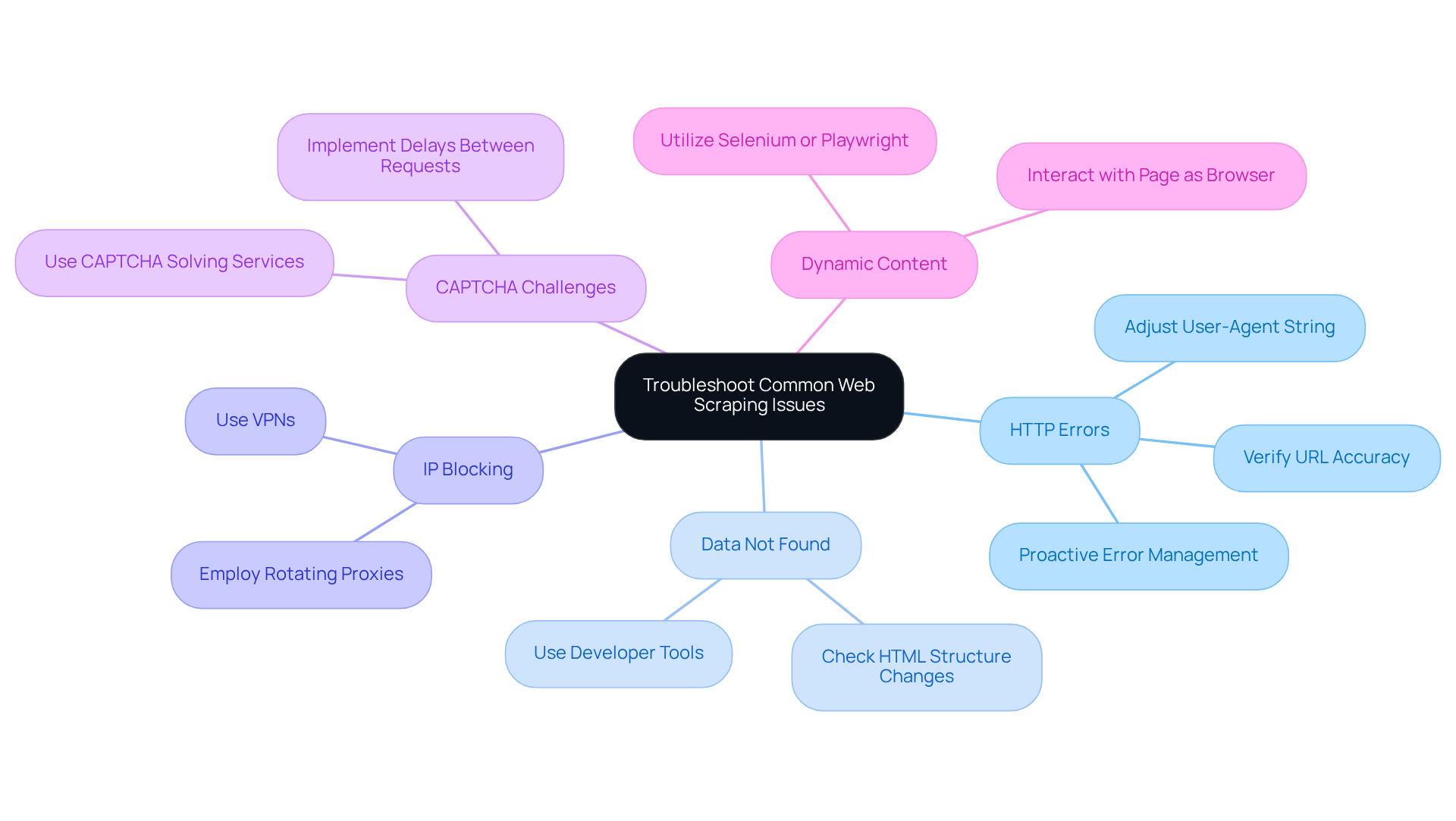
HTTP Errors: If you face errors such as 403 Forbidden or 404 Not Found, first verify the URL for accuracy and ensure that the site allows scraping. Adjusting your user-agent string to mimic a browser can often resolve these issues. Notably, approximately 21.7% of web scrapers report regularly encountering HTTP errors, underscoring the need for proactive error management.
-
Data Not Found: Should your scraper return empty results, check whether the HTML structure has changed. Utilise the browser's developer tools to re-examine the elements, as online pages frequently refresh their layouts.
-
IP Blocking: To prevent IP blocking, consider employing rotating proxies or a VPN to distribute your requests across various IP addresses. This strategy is essential, as about 43% of users regularly encounter IP blocks or CAPTCHA challenges. For instance, e-commerce companies have successfully implemented rotating proxies to monitor competitor pricing without triggering anti-scraping measures.
-
CAPTCHA Challenges: If you encounter CAPTCHAs, consider using services that automatically solve them or implement delays between requests to mimic human behaviour. This approach can significantly reduce the likelihood of being flagged as a bot.
-
Dynamic Content: For websites that load content dynamically (e.g., using JavaScript), consider utilising tools like Selenium or Playwright to interact with the page as a browser would. These tools can effectively manage dynamic content and enhance your data extraction success rates.
By understanding these common issues and their solutions, you can refine your web scraping skills and learn how to do web scraping using python for a smoother experience.
Conclusion
Mastering web scraping with Python provides access to a vast array of information that can significantly enhance business strategies and decision-making processes. Automating data extraction from various websites allows organisations to gain critical insights into market trends, competitor activities, and customer sentiments. This capability transcends mere technical skill; it is an essential asset in today’s data-driven landscape, where effective information utilisation can determine success.
This guide outlines essential steps, from setting up a Python environment and selecting the right tools to writing and refining a web scraper. Key considerations, such as compliance with regulations and the importance of using reliable proxies, are emphasised. By addressing common challenges like HTTP errors, IP blocking, and CAPTCHA, this guide equips users to navigate the complexities of web scraping effectively.
As businesses increasingly depend on data-driven insights to inform their strategies, the ability to scrape and analyse web data effectively will grow in importance. Embracing the techniques discussed not only enhances operational efficiency but also positions organisations to leverage data responsibly and ethically. Engaging with web scraping can create new opportunities and provide a competitive edge in an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping and why is it important?
Web scraping, also known as web harvesting, is an automated method for extracting information from websites. It is important because it provides insights that can drive informed decision-making, enhance competitive analysis, and support comprehensive market research.
How do companies use web data extraction?
Companies utilise web data extraction to monitor competitors' pricing strategies, track product availability, and analyse customer sentiment through social media platforms.
What is the projected trend for digital enterprises regarding web data extraction?
By 2025, over 70% of digital enterprises are expected to leverage publicly accessible data for market intelligence, indicating a growing reliance on web extraction tools.
Can you provide an example of the benefits of web scraping for businesses?
A mid-sized e-commerce retailer reported a 300% increase in ROI on promotional campaigns after implementing a custom data extraction system that monitored competitor websites every 15 minutes.
What role do proxy services play in web scraping?
Proxy services, such as Trusted Proxies, enhance SEO effectiveness and data precision, which are crucial for efficient web extraction. Users have reported faster and more accurate data collection when using reliable proxies.
What regulatory considerations should businesses keep in mind when engaging in web scraping?
Businesses must comply with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to ensure ethical data collection practices.
What is the projected growth of the web data extraction market?
The web data extraction market is projected to grow significantly, reaching between $2.2 billion and $3.5 billion by 2025.
List of Sources
- Understand Web Scraping and Its Importance
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://scrapingdog.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-and-trends)
- Web Scraping Software Market Forecast & Size Insights 2026–2035 (https://businessresearchinsights.com/market-reports/web-scraping-software-market-109339)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://kanhasoft.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-trends-you-need-to-know-in-2025)
- Web Scraping: Unlocking Business Insights In A Data-Driven World (https://forbes.com/councils/forbestechcouncil/2025/01/27/web-scraping-unlocking-business-insights-in-a-data-driven-world)
- Set Up Your Python Environment and Tools
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://scrapingdog.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-and-trends)
- Web Scraping with Python in 2025 - ZenRows (https://zenrows.com/blog/web-scraping-python)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://kanhasoft.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-trends-you-need-to-know-in-2025)
- Case Studies & Projects (https://antrixacademy.com/AboutUs/case_studies.html)
- Build Your Web Scraper: Step-by-Step Instructions
- State of web scraping report 2025 (https://blog.apify.com/state-of-web-scraping)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://scrapingdog.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-and-trends)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://kanhasoft.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-trends-you-need-to-know-in-2025)
- How to Scrape News Articles With AI and Python (https://brightdata.com/blog/web-data/how-to-scrape-news-articles)
- Understanding Web Scraping Legality: Global Insights & Stats (https://browsercat.com/post/web-scraping-legality-global-statistics)
- Troubleshoot Common Web Scraping Issues
- Stop Getting Blocked: 10 Common Web-Scraping Mistakes & Easy Fixes (https://firecrawl.dev/blog/web-scraping-mistakes-and-fixes)
- State of web scraping report 2025 (https://blog.apify.com/state-of-web-scraping)
- Common Web Scraping Challenges and Their Solutions (https://scrapehero.com/web-scraping-challenges)
- Top Web Scraping Challenges in 2025 (https://scrapingbee.com/blog/web-scraping-challenges)
- The State of Web Crawling in 2025: Key Statistics and Industry Benchmarks (https://thunderbit.com/blog/web-crawling-stats-and-industry-benchmarks)




