Introduction
The rapid evolution of technology has transformed how businesses access and utilise data. Screen scraping has emerged as a powerful tool for information extraction. This technique offers significant advantages, including:
- Real-time competitor tracking
- Valuable market insights
However, it also raises critical questions regarding its legality and ethical implications.
As organisations increasingly rely on screen scraping, they must navigate a complex web of legal frameworks and ethical considerations that govern data collection practises. Companies face the challenge of leveraging this method effectively while ensuring compliance and maintaining ethical standards in an ever-changing regulatory landscape.
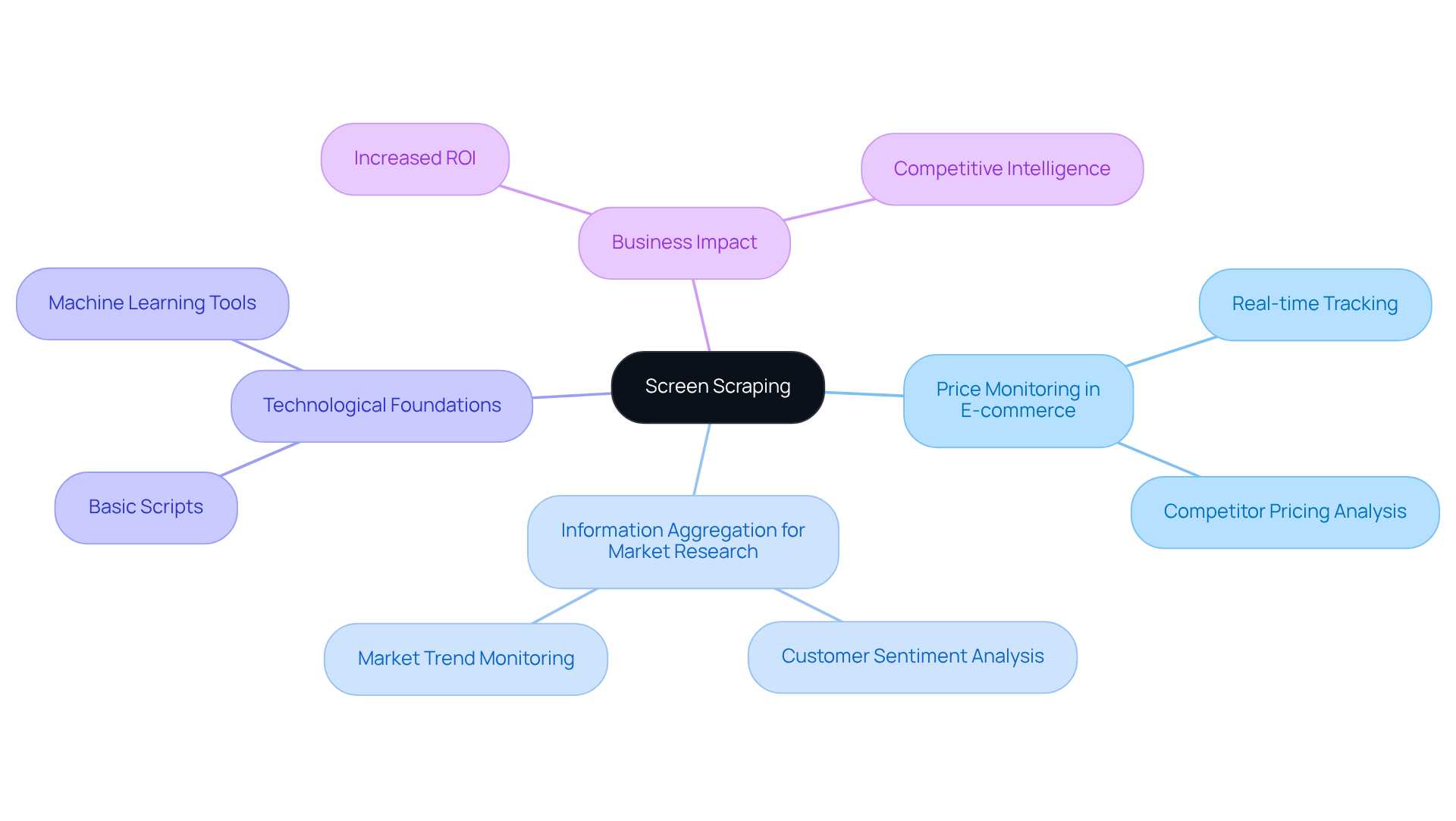
Define Screen Scraping: Mechanisms and Applications
Screen harvesting represents an advanced method of information extraction that captures details displayed on screens, primarily from web pages or applications, for repurposing in various contexts. This process often emulates user behaviour, enabling automated tools to navigate interfaces and extract pertinent information efficiently.
Key applications of screen extraction include:
- Price Monitoring in E-commerce: Businesses utilise this method to track competitor pricing in real-time.
- Information Aggregation for Market Research: This involves gathering insights from customer sentiment on social media platforms.
The technology underpinning screen extraction varies from basic scripts that automate browser actions to sophisticated tools that leverage machine learning for enhanced data extraction and normalisation. For example, a mid-sized e-commerce retailer developed a custom data extraction system that monitored competitor websites every 15 minutes, resulting in a 300% increase in ROI on promotional campaigns.
As companies increasingly rely on screen extraction for competitive intelligence, the effectiveness of these tools is underscored by their ability to provide timely and actionable insights, making them essential in today’s data-driven environment.
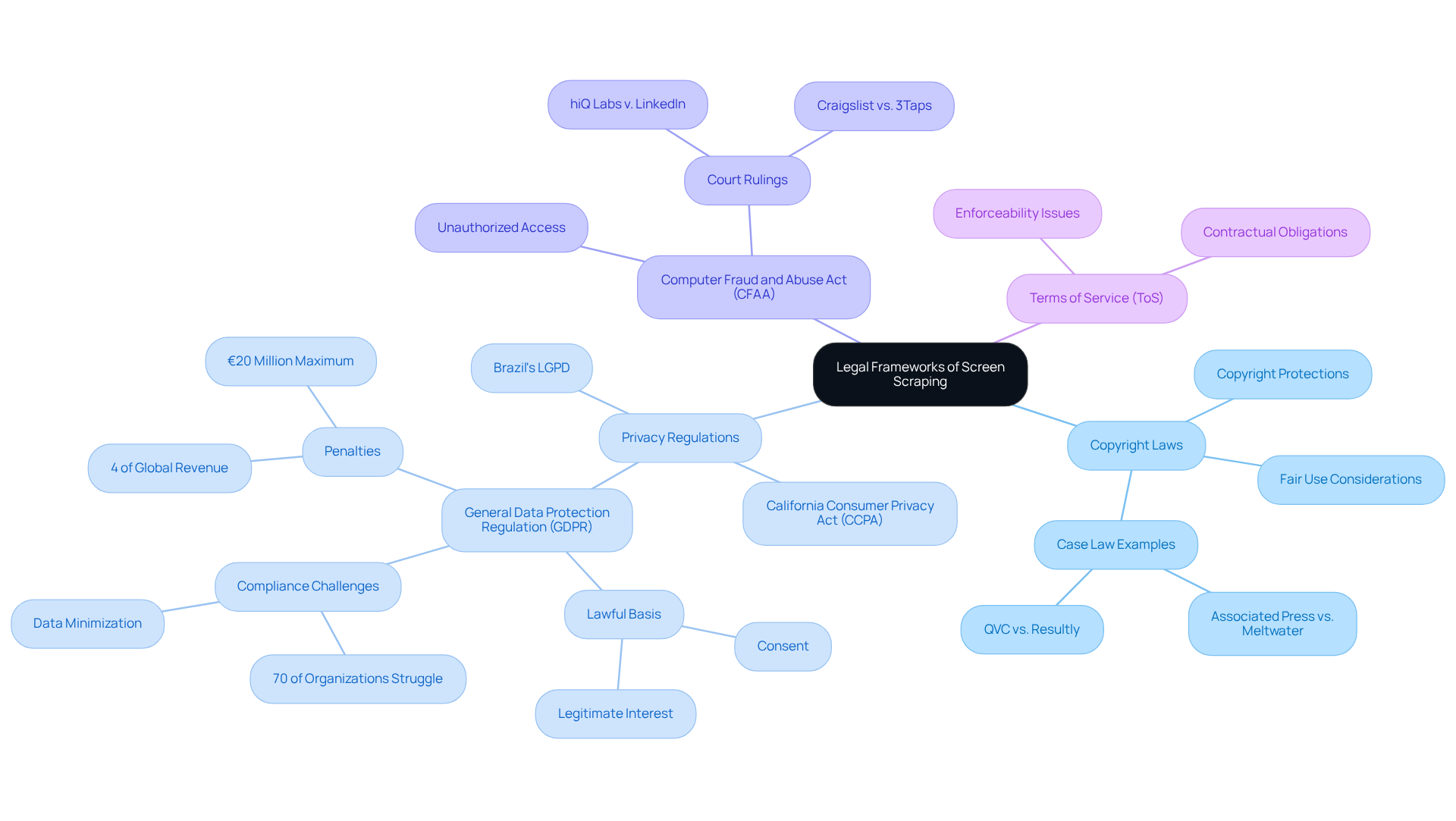
Examine Legal Frameworks: Understanding the Legality of Screen Scraping
The determination of whether is screen scraping legal is influenced by a complex interplay of legal frameworks, including copyright laws, privacy regulations, and terms of service agreements. In many jurisdictions, collecting publicly accessible information is generally permitted; however, complications arise when personal information is involved. Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the EU, the collection of personal information necessitates a lawful basis, such as consent or legitimate interest. Notably, statistics on GDPR compliance reveal that over 70% of organisations encounter difficulties in fully adhering to its requirements, underscoring the challenges businesses face in this domain. Furthermore, penalties for non-compliance with GDPR can reach up to 4% of global annual revenue or €20 million, whichever is higher, highlighting the financial implications of compliance.
The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the United States introduces additional risks, particularly if data extraction is interpreted as unauthorised access to computer systems. Recent court rulings, including the landmark hiQ Labs v. LinkedIn case, have clarified that accessing publicly available information does not constitute unauthorised access under the CFAA, leading to discussions about whether is screen scraping legal and offering some legal protection for scrapers. However, the evolving regulatory landscape requires businesses to remain vigilant and informed about their obligations.
Experts emphasise that companies must implement optimal strategies for GDPR compliance in their scraping activities. This includes:
- Respecting robots.txt files
- Limiting information collection to what is essential
- Ensuring transparency in processing
As Kevin Sahin notes, focusing on publicly accessible information and adhering to these guidelines can significantly mitigate legal risks. As the regulatory environment continues to evolve, understanding if is screen scraping legal is crucial for companies engaged in screen data extraction to minimise risks and uphold ethical standards.
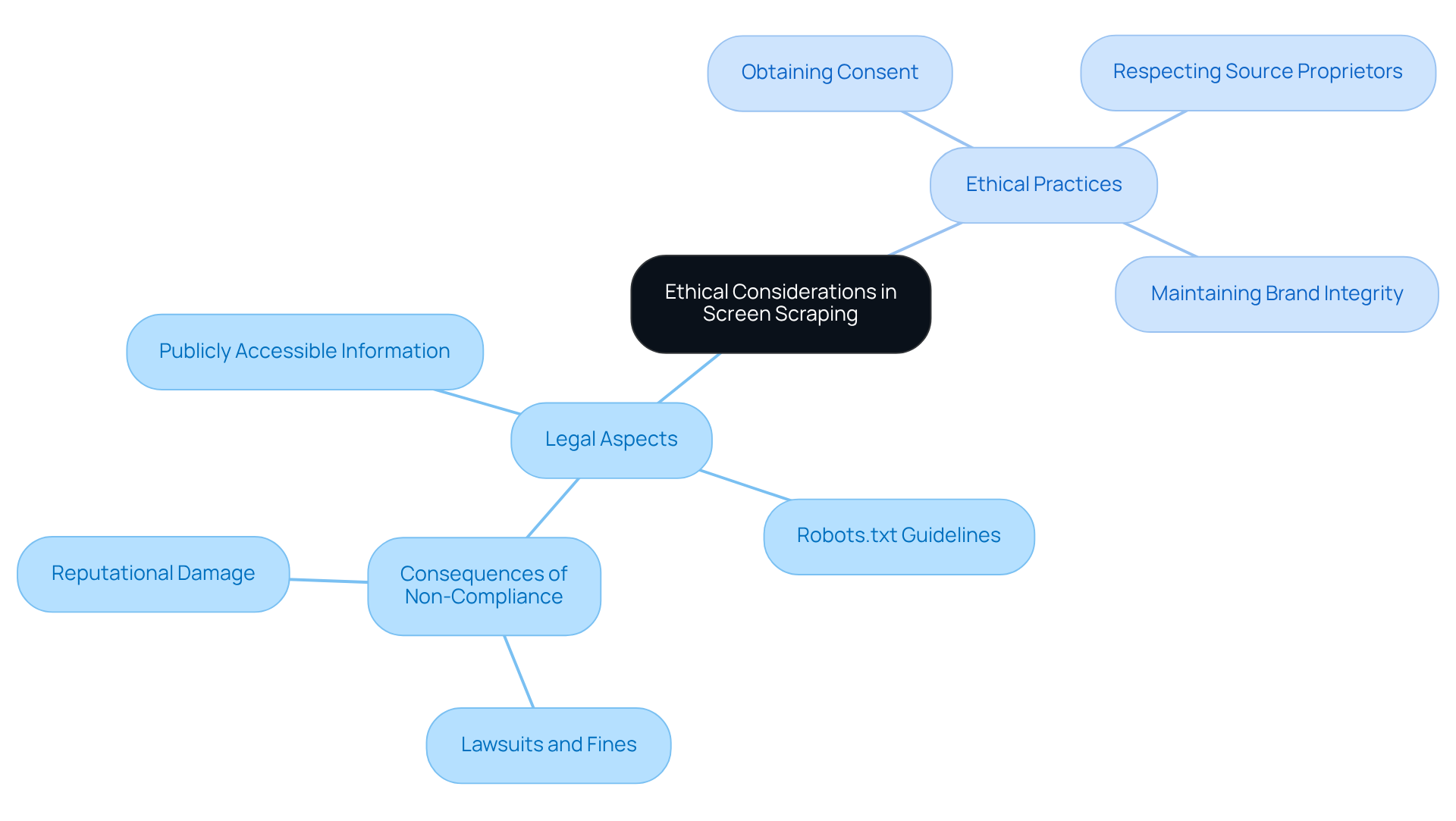
Contrast Ethical Considerations: Legal vs. Ethical Scraping Practices
While screen extraction may be legal under certain conditions, the inquiry into whether is screen scraping legal presents a more complex ethical challenge. Legally, gathering publicly accessible information typically does not breach laws; however, when considering the question of 'is screen scraping legal', ethical practices necessitate respect for the source and its proprietors. For instance, companies like Actowiz Solutions have established protocols to ensure responsible information usage, including obtaining explicit consent from website owners prior to harvesting. This approach not only aligns with ethical standards but also helps maintain brand integrity and user trust.
The significance of permission in information extraction cannot be overstated. Ethical extraction practices involve adhering to robots.txt guidelines and ensuring that the information gathered does not violate privacy rights. As Jagdish Mohite, a Principal Security Consultant, observes, 'One of the primary concerns is whether is screen scraping legal and the financial risks associated with data extraction.' Failure to comply with these ethical standards can result in considerable reputational harm, as emphasized in the case study on 'Legal and Financial Risks of Content Scraping,' where unauthorized information harvesting led to lawsuits and penalties.
In 2026, as the demand for real-time information continues to rise, with the global web extraction software market valued at $875.46 million, organizations must carefully navigate the balance between utilizing information for competitive advantage and upholding ethical standards. By fostering a culture of responsible data use, companies can mitigate risks and enhance their reputation in an increasingly data-driven marketplace.
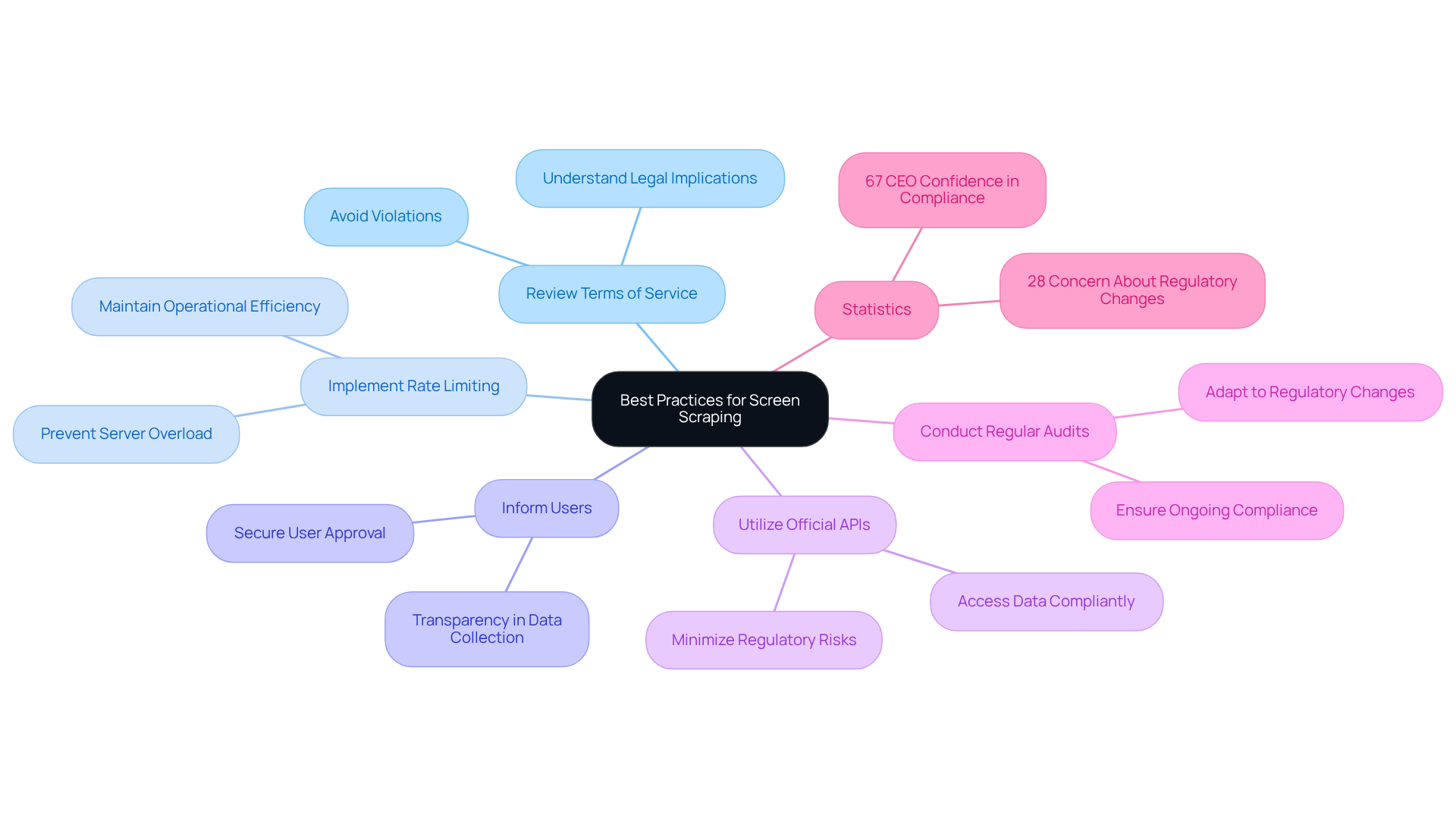
Implement Best Practices: Navigating Legal and Ethical Screen Scraping
To effectively navigate the regulatory and ethical landscape, businesses must consider whether screen scraping is legal and adopt several optimal strategies. First and foremost, it is crucial to review and adhere to the terms of service of the websites being scraped, particularly to determine if screen scraping is legal, as violations can result in significant legal repercussions. Notably, 28% of organisations express concern about missing regulatory changes in their compliance programmes, underscoring the necessity for vigilance in this area.
Implementing rate limiting is another essential strategy to prevent overwhelming servers and to respect the resources of the websites. Companies like Zyte have successfully integrated rate limiting into their data collection strategies, ensuring compliance while maintaining operational efficiency. Clarity is also vital; organisations should inform users about their information collection methods and secure approval when necessary, in line with the growing emphasis on ethical information usage.
When available, utilising official APIs offers a more reliable and compliant method for accessing data, thereby minimising the risk of regulatory issues associated with data collection. Regular audits of scraping practices are critical to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving legal standards, especially regarding the question of whether screen scraping is legal. As 67% of CEOs express confidence in their organisation's adherence to AI regulations, maintaining a proactive stance on compliance can significantly enhance a company's reputation and operational integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, screen scraping occupies a critical space where technology meets legality, offering both significant opportunities and notable challenges for businesses operating in the digital realm. It is crucial for companies to grasp the legal nuances surrounding screen scraping to effectively harness this powerful tool while navigating the intricate landscape of legal and ethical considerations.
This article has explored the mechanisms and applications of screen scraping, underscoring its vital role in areas such as price monitoring and market research. Furthermore, it has examined the legal frameworks that govern this practise, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) in the United States. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid severe penalties. Ethical considerations also play a significant role, with the necessity for explicit consent and adherence to established best practises highlighting the importance of maintaining trust and integrity in data usage.
As the demand for real-time information continues to escalate, organisations must prioritise ethical practises alongside legal compliance. By implementing strategies such as rate limiting, respecting website terms of service, and utilising official APIs, businesses can mitigate legal risks while enhancing their reputation in an increasingly data-driven environment. Embracing these principles will ensure that screen scraping becomes a valuable asset rather than a liability, fostering a culture of responsible data use that benefits all stakeholders involved.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is screen scraping?
Screen scraping is an advanced method of information extraction that captures details displayed on screens, primarily from web pages or applications, for repurposing in various contexts.
How does screen scraping work?
Screen scraping emulates user behaviour, allowing automated tools to navigate interfaces and efficiently extract pertinent information.
What are some key applications of screen scraping?
Key applications include price monitoring in e-commerce to track competitor pricing in real-time and information aggregation for market research, such as gathering insights from customer sentiment on social media platforms.
What technology is used in screen scraping?
The technology ranges from basic scripts that automate browser actions to sophisticated tools that utilise machine learning for enhanced data extraction and normalisation.
Can you provide an example of screen scraping in use?
A mid-sized e-commerce retailer developed a custom data extraction system that monitored competitor websites every 15 minutes, resulting in a 300% increase in ROI on promotional campaigns.
Why is screen scraping important for companies?
Screen scraping is essential for companies as it provides timely and actionable insights, which are crucial for competitive intelligence in today’s data-driven environment.
List of Sources
- Define Screen Scraping: Mechanisms and Applications
- AI Web Scraping: The Ultimate 2026 Guide - AI-Driven Data Intelligence & Web Scraping Solutions (https://hirinfotech.com/ai-web-scraping-the-ultimate-2026-guide)
- Oxylabs launches AI Studio to simplify web scraping for all users (https://ecommercenews.uk/story/oxylabs-launches-ai-studio-to-simplify-web-scraping-for-all-users)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://kanhasoft.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-trends-you-need-to-know-in-2025)
- Web Scraping Trends for 2025 and 2026 (https://ficstar.medium.com/web-scraping-trends-for-2025-and-2026-0568d38b2b05?source=rss------ai-5)
- State of Web Scraping 2026: Trends, Challenges & What’s Next (https://browserless.io/blog/state-of-web-scraping-2026)
- Examine Legal Frameworks: Understanding the Legality of Screen Scraping
- The $2 Billion ‘Free-Rider’ Problem: Why AI Scraping is Now a Boardroom Crisis (https://corporatecomplianceinsights.com/free-rider-problem-ai-scraping-boardroom-crisis)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2026 (https://dataprixa.com/web-scraping-statistics-trends)
- Is Web Scraping Legal in 2026? Best Practices for Legal Web Scraping (https://dataprixa.com/is-web-scraping-legal)
- Is Web Scraping Legal? Key Insights and Guidelines You Need to Know (https://scrapingbee.com/blog/is-web-scraping-legal)
- The state of web scraping in the EU | IAPP (https://iapp.org/news/a/the-state-of-web-scraping-in-the-eu)
- Contrast Ethical Considerations: Legal vs. Ethical Scraping Practices
- The Ethics and Legality of Web Scraping: Navigating the Gray Areas - DCP (https://dcpweb.co.uk/blog/the-ethics-and-legality-of-web-scraping-navigating-the-gray-areas)
- Global privacy authorities issue follow-up joint statement on data scraping after industry engagement (https://ico.org.uk/about-the-ico/media-centre/news-and-blogs/2024/10/global-privacy-authorities-issue-follow-up-joint-statement-on-data-scraping-after-industry-engagement)
- Global Regulators Urge Social Media Firms to Enhance Data Protection Against Scraping | nquiringminds Ltd (https://nquiringminds.com/ai-legal-news/global-regulators-urge-social-media-firms-to-enhance-data-protection-against-scraping)
- The Hidden Costs and Ethical Pitfalls of Content Scraping | Akamai (https://akamai.com/blog/security/the-hidden-costs-and-ethical-pitfalls-of-content-scraping)
- 2026 Web Scraping Industry Report | AI Data Trends | Actowiz Solutions (https://actowizsolutions.com/web-scraping-industry-report-data-first-ai-revolution.php)
- Implement Best Practices: Navigating Legal and Ethical Screen Scraping
- Is Web Scraping Legal? Understanding the Law for UK Businesses and Entrepreneurs | Sprintlaw UK (https://sprintlaw.co.uk/articles/is-web-scraping-legal-understanding-the-law-for-uk-businesses-and-entrepreneurs)
- Is Web Scraping Legal? Everything You Need to Know (https://companionlink.com/blog/2026/01/is-web-scraping-legal-everything-you-need-to-know)
- Is Web Scraping Legal? Navigating Terms of Service and Best Practices (https://ethicalwebdata.com/2025/01/27/is-web-scraping-legal-navigating-terms-of-service-and-best-practices)
- AI’s legal frontier: What Europe’s privacy regulators say about scraping personal data (https://zyte.com/blog/ai-personal-data-scraping-europe-guidance)
- 130+ Compliance Statistics & Trends to Know for 2026 (https://secureframe.com/blog/compliance-statistics)




