Introduction
Understanding the nuances of data integration methods is crucial in today’s data-driven landscape. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) represent two distinct approaches that cater to different organisational needs. These methods particularly impact data quality, compliance, and processing speed.
As businesses grapple with the ever-increasing volume and complexity of data, the decision of which method to employ becomes pivotal. Organisations must assess their unique requirements to determine the most suitable approach. Key differences between ETL and ELT can significantly influence this choice, guiding businesses toward the method that best aligns with their operational goals.
Define ETL and ELT: Core Concepts in Data Management
The traditional integration process known as ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) involves extracting information from various sources, transforming it into a suitable format, and loading it into a warehouse. This method excels in environments where information integrity and compliance are critical, particularly for structured information. While specific statistics for 2026 are not provided, ETL is often favoured in regulated sectors such as healthcare and finance, where strict information governance is essential.
Conversely, the processes of ETL and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) reverse this sequence. In ELT, information is first extracted and loaded into the target system, such as a data lake or repository, before undergoing transformation as needed. This method leverages the computing capabilities of contemporary cloud platforms, making it especially efficient for handling substantial amounts of unorganised or partially organised information. Although particular forecasts for 2026 are not accessible, ELT is increasingly embraced by companies seeking flexibility and scalability in information handling.
Understanding these essential concepts of ETL and ELT is crucial, as they highlight the fundamental distinctions in information handling methodologies. The organised approach and compliance features of ETL are frequently favoured, whereas ELT, part of the discussion on ETL and ELT, provides speed and flexibility to address the evolving requirements of analytics and business intelligence. Additionally, a hybrid approach can effectively combine ETL and ELT for sensitive information requiring preprocessing as well as for exploratory analytics and large-scale processing.
Contrast ETL and ELT: Key Differences in Processes
The primary difference between ETL and ELT is the order of operations. In both ETL and ELT, content is transformed before it is loaded into the data warehouse. This transformation process can be resource-intensive and may necessitate dedicated infrastructure to manage the workload. In scenarios where information quality and compliance are critical, ETL and ELT are often preferred as they allow for thorough cleansing and validation prior to storage.
Conversely, ETL and ELT processes load raw information directly into the warehouse or lake, where it is transformed as needed. This approach is generally faster and more flexible, enabling organisations to take advantage of the scalability offered by cloud environments. ELT is particularly beneficial for real-time analytics and when handling large datasets that may not conform to predefined schemas.
In summary, the processes of ETL and ELT are characterised by:
- ETL's organised and regulated nature
- ELT's greater flexibility and speed, making it well-suited for modern information architectures.
Evaluate Pros and Cons: Strengths and Weaknesses of ETL vs ELT
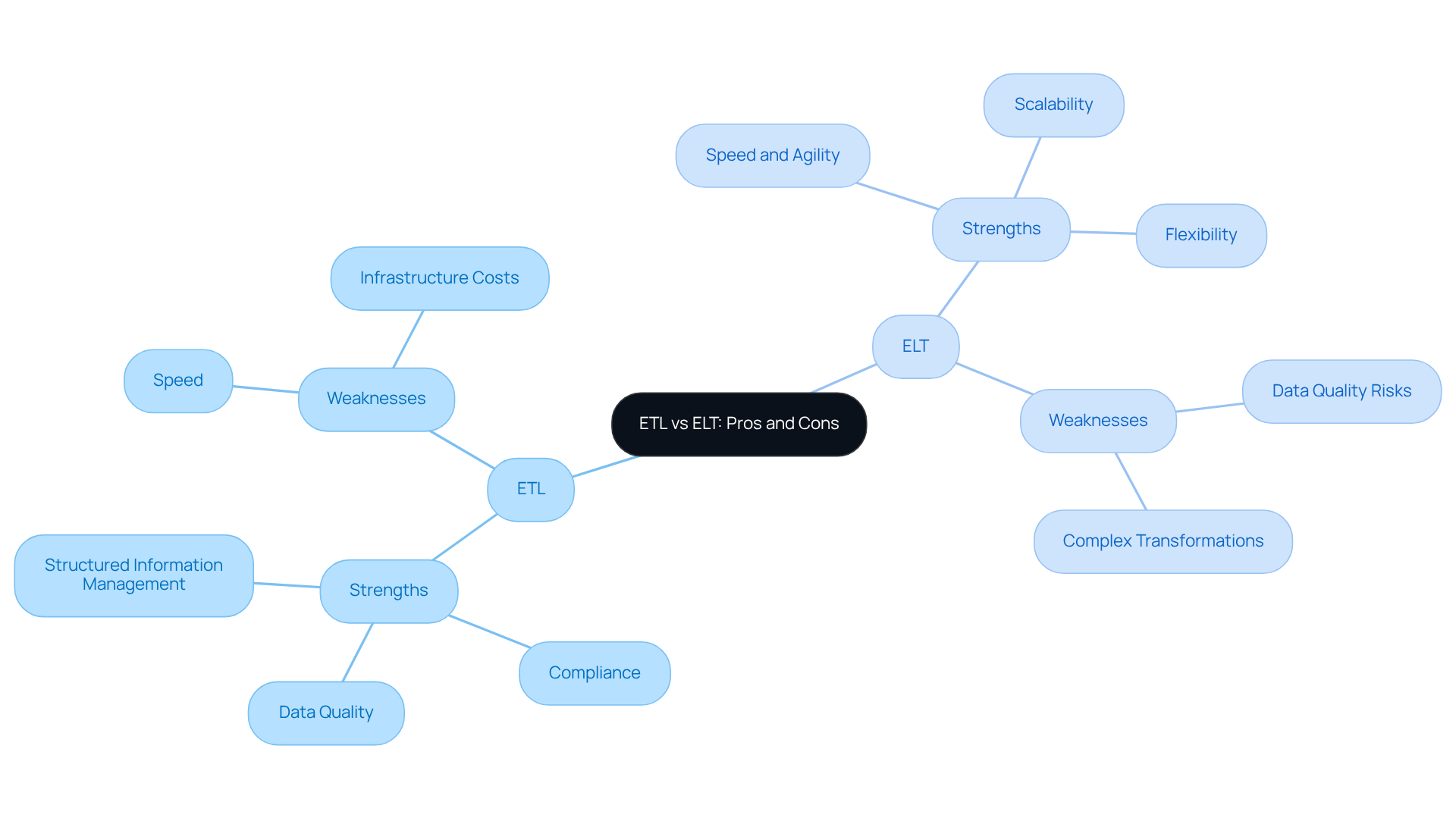
When evaluating ETL, its strengths include:
- Data Quality: ETL ensures high data quality through rigorous transformation processes before loading, making it particularly effective in regulated environments where data integrity is paramount. According to Gartner, organisations report significant losses due to poor information quality, averaging $12.9 million annually, which highlights the importance of ETL and ELT in maintaining information standards.
- Compliance: It is well-suited for industries with strict regulatory requirements, as information can be cleansed and masked before storage, ensuring adherence to compliance standards. This is crucial in sectors like finance and healthcare, where regulatory scrutiny is intense.
- Structured Information Management: ETL excels in environments where information is organised and well-defined, providing reliable outputs for business intelligence and reporting. A worldwide retail firm, for example, utilises ETL each night to guarantee clean, unified information for precise reporting.
However, ETL also has weaknesses:
- Speed: The transformation step can introduce latency, making ETL less suitable for real-time data processing, which is increasingly demanded in today's fast-paced business landscape. Gartner observes that ETL processes may become bottlenecks as volumes of information rise.
- Infrastructure Costs: ETL often requires dedicated servers and complex orchestration, leading to higher operational costs, particularly in large-scale implementations. Organisations may face challenges in scaling ETL solutions effectively.
In contrast, ELT offers several advantages:
- Speed and Agility: ELT allows for faster data ingestion and processing, making it ideal for real-time analytics, which is crucial for organisations needing immediate insights. For example, a media streaming service collects millions of semi-structured logs per hour using ELT, enabling rapid analysis.
- Scalability: Utilising cloud infrastructure, ELT can manage substantial volumes of information without significant performance degradation, accommodating the increasing requirements of businesses. This scalability is essential as organisations increasingly adopt cloud-first strategies.
- Flexibility: ELT can accommodate various types of information, including unstructured and semi-structured formats, enabling organisations to adapt to diverse sources and structures. This flexibility supports evolving analytical requirements and enhances information exploration capabilities.
However, ELT has its drawbacks:
- Data Quality Risks: Since data is loaded in its raw form, there may be challenges in ensuring data quality and consistency, which can lead to operational inefficiencies. Organisations must implement robust governance measures to mitigate these risks.
- Complex Transformations: Some intricate transformations may be more difficult to execute in ELT than in ETL, potentially complicating workflows for advanced analytics. As noted by industry experts, careful planning is required to manage these complexities effectively.
Determine Suitability: When to Choose ETL or ELT
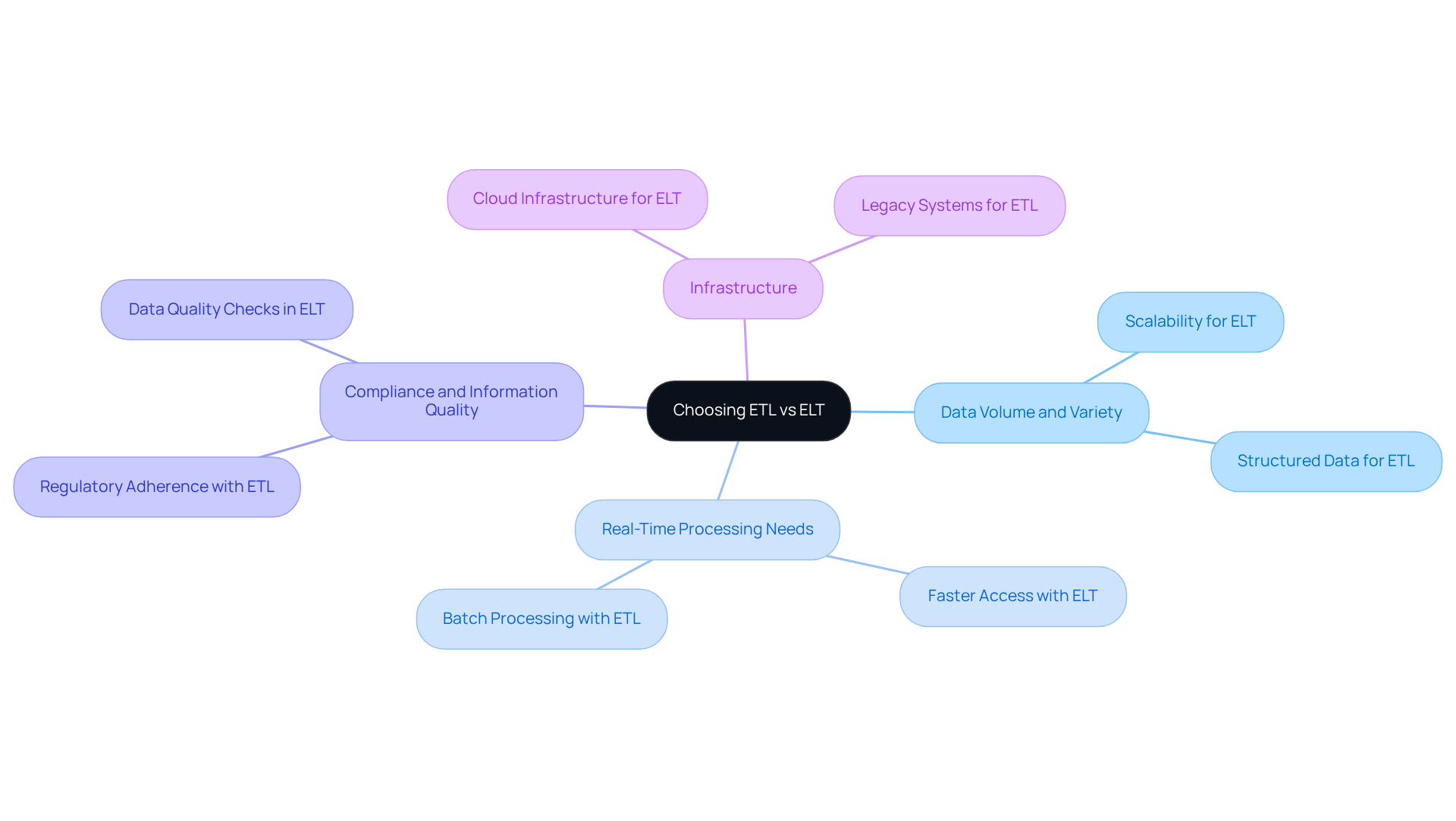
Choosing between ETL and ELT involves several critical considerations:
-
Data Volume and Variety: Organisations managing large volumes of diverse data types often find ELT to be the superior choice due to its inherent scalability and flexibility. ELT can efficiently manage structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information, making it ideal for dynamic environments. In contrast, ETL is more appropriate for situations where information is primarily structured and well-defined, allowing for effective management of smaller datasets.
-
Real-Time Processing Needs: For businesses that require real-time analytics, ELT is frequently favoured. This approach allows prompt access to unrefined information and promotes quicker execution times, which is crucial for organisations striving to obtain insights rapidly. As real-time processing becomes increasingly mandatory, with growth rates of approximately 20-22% CAGR, ELT's capabilities align well with these demands.
-
Compliance and Information Quality: When regulatory adherence and information quality are top priorities, ETL typically emerges as the better option. This approach guarantees comprehensive information cleansing and validation prior to storage, which is essential for sectors with stringent compliance requirements. Appstractor enhances this process by hashing rows, dropping duplicates, and running schema validation before delivery. This meticulous approach not only ensures that information is clean and de-duplicated but also supports organisations in making informed decisions between ETL and ELT by emphasising integrity. As mentioned by Gartner, "ETL excels when information quality, compliance, and governance are top priorities, especially in regulated sectors or when dealing with structured datasets."
-
Infrastructure: The existing infrastructure plays a significant role in determining the appropriate method. Organisations equipped with robust cloud infrastructure can leverage ELT's capabilities for enhanced performance and agility. Conversely, those operating with legacy systems may find ETL more compatible with their workflows, allowing for smoother integration with established processes.
Ultimately, the choice between ETL and ELT should align with the organisation's overarching information strategy, operational requirements, and long-term objectives involving ETL and ELT. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can select the most suitable approach to optimise their data integration efforts.
Conclusion
The distinctions between ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) processes are crucial in data management. ETL is often favoured for its structured approach and compliance capabilities, especially in regulated industries. On the other hand, ELT provides the speed and flexibility needed for modern data environments. Understanding when to use each method is vital for organisations looking to optimise their data integration strategies.
Key insights reveal that:
- ETL excels in ensuring data quality and compliance, making it ideal for structured data in regulated sectors.
- ELT is adept at managing large volumes of unstructured data with agility, aligning well with the demand for real-time analytics.
The choice between ETL and ELT ultimately depends on specific organisational needs, including:
- Data volume
- Processing speed
- Compliance requirements
- Existing infrastructure
In a rapidly evolving data landscape, the decision to adopt ETL or ELT should stem from a thorough evaluation of these factors. Organisations must reflect on their long-term data strategy and operational requirements to choose the most effective approach. By doing so, they can enhance their data integration efforts and maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do ETL and ELT stand for in data management?
ETL stands for Extract, Transform, Load, while ELT stands for Extract, Load, Transform.
How does the ETL process work?
In the ETL process, information is extracted from various sources, transformed into a suitable format, and then loaded into a data warehouse.
In what environments is ETL particularly favoured?
ETL is often favoured in regulated sectors such as healthcare and finance, where information integrity and compliance are critical.
How does the ELT process differ from ETL?
In the ELT process, information is first extracted and loaded into the target system, such as a data lake, before undergoing transformation as needed.
What advantages does ELT provide?
ELT leverages the computing capabilities of modern cloud platforms, making it efficient for handling large amounts of unorganised or partially organised information, providing flexibility and scalability.
Why is it important to understand ETL and ELT?
Understanding ETL and ELT is crucial as they highlight the fundamental distinctions in information handling methodologies, impacting how organisations manage data for analytics and business intelligence.
Can ETL and ELT be used together?
Yes, a hybrid approach can effectively combine ETL and ELT for sensitive information that requires preprocessing as well as for exploratory analytics and large-scale processing.
List of Sources
- Define ETL and ELT: Core Concepts in Data Management
- Data Integration Market Share, Forecast | Growth Analysis & Opportunities [2030] (https://marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/data-integration-market-61793560.html)
- Data Analytics Enhancement Stats via ETL — 35 Statistics Every Data Leader Should Know in 2026 (https://integrate.io/blog/data-analytics-enhancement-stats-via-etl)
- ETL vs ELT: What's the difference and why it matters | dbt Labs (https://getdbt.com/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- ETL vs ELT: Differences & Which to Use (https://matillion.com/blog/better-faster-smarter-elt-vs-etl)
- ETL vs ELT: 5 Critical Differences (https://integrate.io/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- Contrast ETL and ELT: Key Differences in Processes
- ETL vs ELT: The Definitive Guide to Key Differences (2026) (https://improvado.io/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- ETL vs ELT: Differences & Which to Use (https://matillion.com/blog/better-faster-smarter-elt-vs-etl)
- ETL vs ELT: Dive Deeper into Two Data Processing Approaches (https://databricks.com/discover/etl/vs-elt)
- ETL vs ELT: What's the difference and why it matters | dbt Labs (https://getdbt.com/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- ETL vs ELT: Key Differences, Comparisons, & Use Cases (https://rivery.io/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- Evaluate Pros and Cons: Strengths and Weaknesses of ETL vs ELT
- ELT vs ETL Comparison Statistics – 40+ Key Data Points Every Data Leader Should Know in 2026 (https://integrate.io/blog/elt-vs-etl-comparison-statistics)
- Data Quality Improvement Stats from ETL – 50+ Key Facts Every Data Leader Should Know in 2026 (https://integrate.io/blog/data-quality-improvement-stats-from-etl)
- ETL vs ELT: Key Differences, Pros & Cons (https://dqlabs.ai/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- ETL vs ELT Difference: Which Approach Fits into Modern AI Workflows - AI Enabled Data Integrations and Analytics (https://bizdata360.com/etl-vs-elt-difference)
- Data Analytics Enhancement Stats via ETL — 35 Statistics Every Data Leader Should Know in 2026 (https://integrate.io/blog/data-analytics-enhancement-stats-via-etl)
- Determine Suitability: When to Choose ETL or ELT
- ELT vs ETL Comparison Statistics – 40+ Key Data Points Every Data Leader Should Know in 2026 (https://integrate.io/blog/elt-vs-etl-comparison-statistics)
- ETL vs ELT: Differences & Which to Use (https://matillion.com/blog/better-faster-smarter-elt-vs-etl)
- ETL vs ELT: Key Differences, Pros & Cons (https://dqlabs.ai/blog/etl-vs-elt)
- Choosing Between ETL vs ELT for Data Integration Success | Alation (https://alation.com/blog/etl-vs-elt-whats-the-difference)
- How to decide between ETL and ELT for data management needs (https://blogs.opentext.com/how-to-decide-between-etl-and-elt-for-data-management-needs)




