Introduction
The realm of web scraping is evolving swiftly, and the selection of programming language can significantly influence the efficiency of data extraction processes. Among the leading contenders - Python, Go, and Rust - each language presents unique advantages tailored to various project requirements. As developers evaluate their choices, a pivotal question emerges: which language stands out as the fastest for web scraping? This article provides a comparative analysis of these three languages, examining their performance, usability, and distinctive strengths to assist programmers in making informed decisions regarding their web scraping projects.
Understanding Web Scraping Languages: An Overview
Web scraping is a technique for extracting data from websites, and selecting the fastest web scraping language can significantly influence the efficiency and effectiveness of this process. Among the three leading languages for web scraping - Python, Go, and Rust - Python is often considered the fastest web scraping language, each having its own unique advantages and challenges.
Python
- Ease of Use: Python is renowned for its clarity and simplicity, making it a preferred choice for both novices and experienced programmers.
- Robust Libraries: It boasts a strong collection of libraries, such as BeautifulSoup and Scrapy, which facilitate web scraping tasks.
- Community Support: Extensive community resources ensure that programmers can quickly find solutions to challenges.
- Adoption Rate: As of 2025, Python holds a leading position as the fastest web scraping language, with a 69.6% adoption rate among developers, reflecting its strong foothold in the industry.
Go
- Performance: Go is recognised for its performance and concurrency capabilities, utilising goroutines to manage multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Scalability: This feature makes it particularly well-suited for large-scale data extraction operations, especially when utilising the fastest web scraping language, where speed is paramount.
- Market Position: As the global web data extraction market continues to grow, Go's lightweight architecture positions it as a strong contender for high-performance applications.
Rust
- High Performance: Rust combines high performance with memory safety, making it ideal for applications that require both speed and reliability.
- Error Prevention: Its strict compile-time checks help prevent common programming errors, which is advantageous for developing robust extraction tools.
- Emerging Adoption: While Rust is gaining traction, its adoption in web data extraction is still emerging, with developers increasingly recognising its potential for complex tasks.
Understanding the fundamental characteristics of these languages is crucial for assessing their appropriateness for different web extraction tasks, including identifying the fastest web scraping language. As the landscape evolves, the choice between Go and Rust will depend on specific project requirements, team expertise, and the desired balance between speed, reliability, and ease of use.
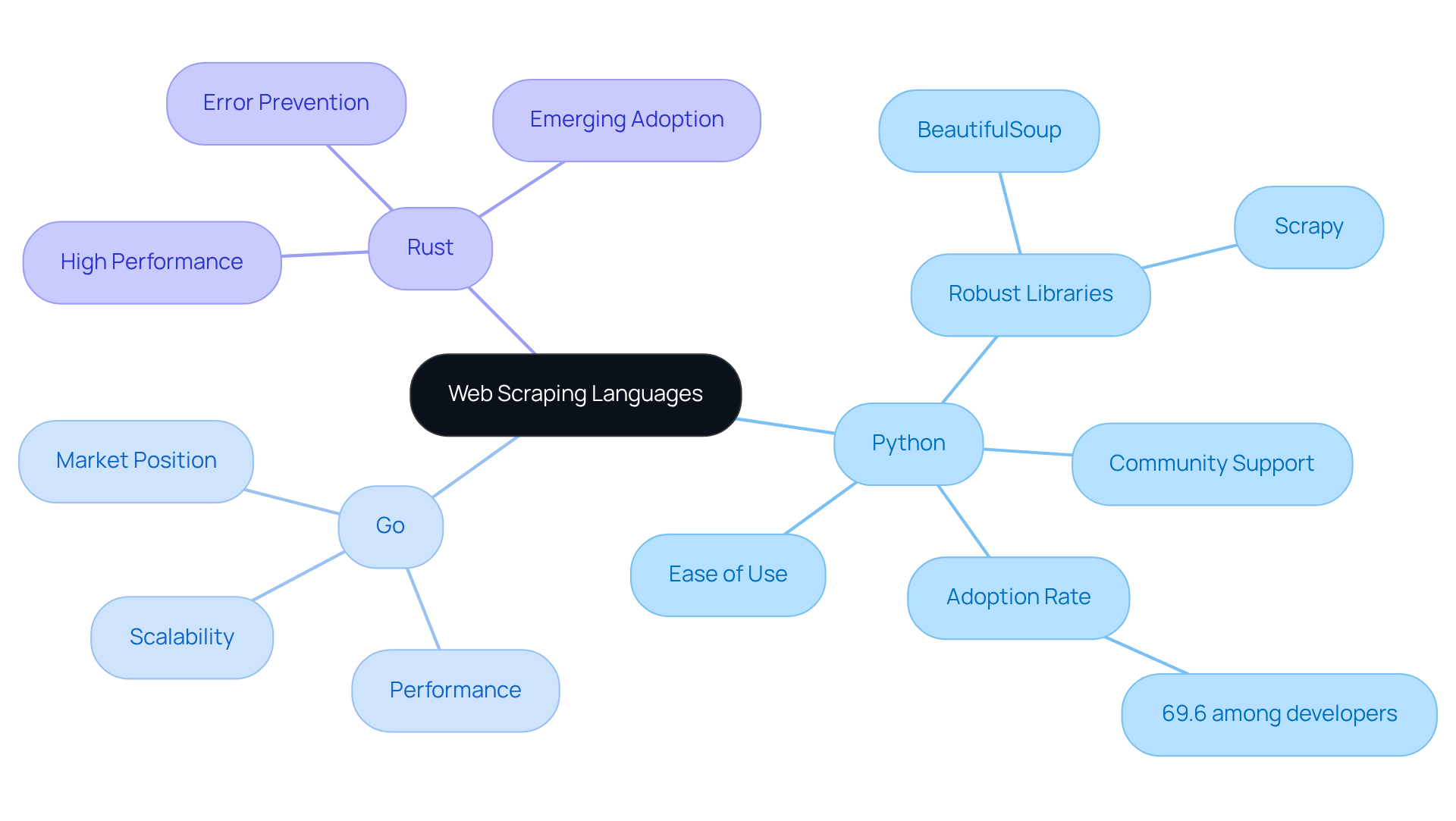
Evaluating Python: Strengths and Limitations in Web Scraping
Python remains a leading choice for data extraction, recognised for its user-friendly syntax and extensive library ecosystem.
- Ease of Use: Python's straightforward syntax enhances accessibility, enabling beginners to swiftly write and test extraction scripts. This simplicity is a significant advantage for programmers looking to implement data extraction solutions without facing a steep learning curve.
- Rich Ecosystem: The language features a robust array of libraries, including BeautifulSoup, Scrapy, and Requests, which streamline HTML parsing, request management, and data extraction. These tools empower developers to handle various extraction tasks efficiently, ranging from simple data retrieval to intricate web crawling operations.
- Community Support: With a large and active community, users gain access to a wealth of resources, such as tutorials, forums, and shared knowledge. This support network proves invaluable for troubleshooting and enhancing data collection projects.
However, Python does have its limitations:
- Performance: While Python excels in small to medium-scale scraping tasks, it may face challenges under high-performance demands, particularly when dealing with large data volumes. The interpreted nature of the language can result in slower execution times compared to compiled languages.
- Concurrency: The Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) restricts the execution of multiple threads simultaneously, which can impede performance in highly concurrent data collection tasks. This limitation may require the adoption of asynchronous programming or alternative strategies to achieve the desired performance levels.
In conclusion, Python is recognised as the fastest web scraping language and an excellent choice for web data extraction, particularly for those who value ease of use and rapid development. Its extensive library support and community resources make it a preferred language for many developers, despite its performance constraints in certain high-demand scenarios.
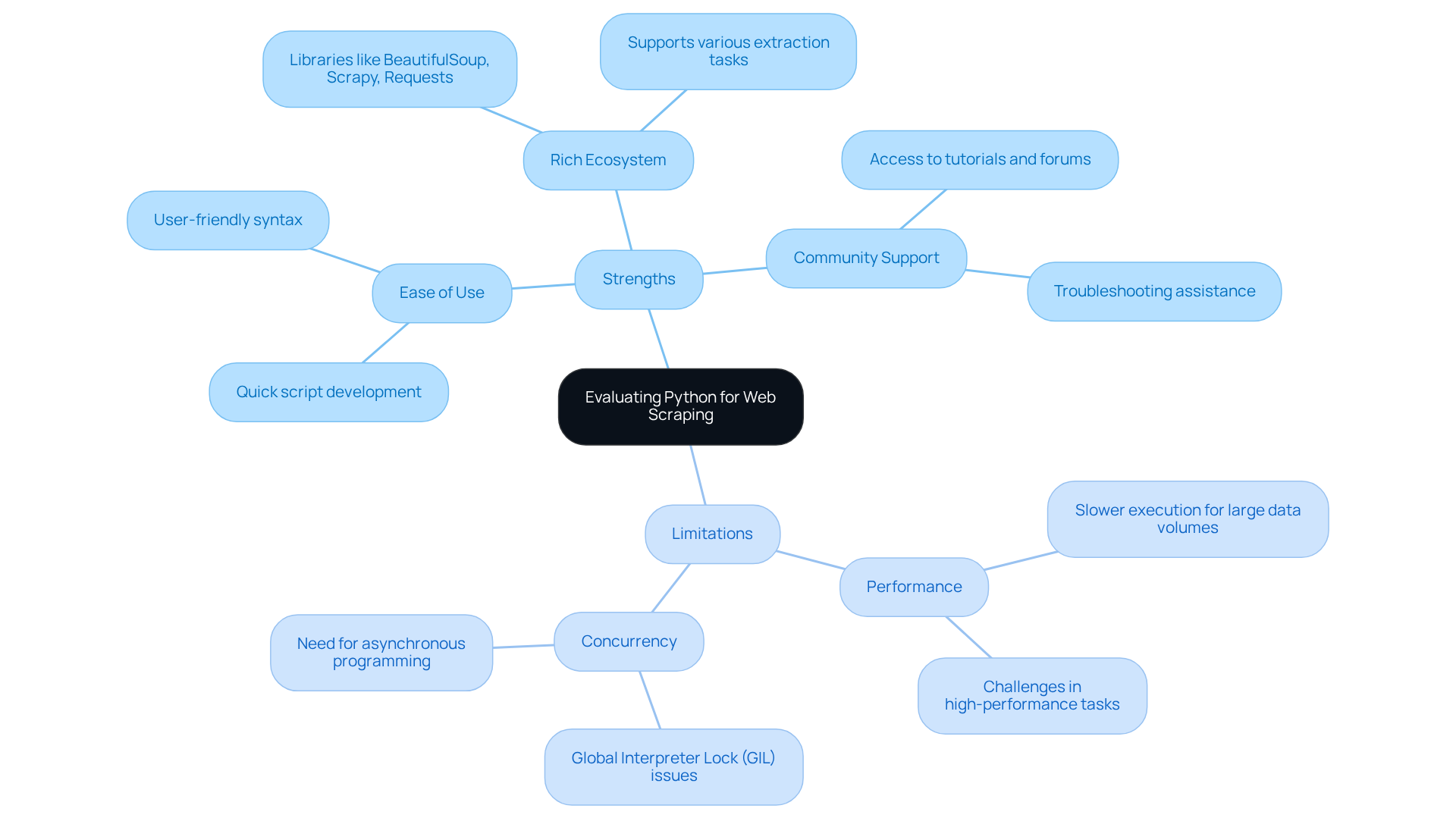
Assessing Go: Performance and Use Cases for Web Scraping
Go, or Golang, has emerged as the fastest web scraping language in the web data extraction community, primarily due to its exceptional performance and efficiency.
Performance:
- Speed: As a compiled language, Go typically executes faster than interpreted languages like Python. Recent benchmarks indicate that Go, considered the fastest web scraping language, can surpass Python by as much as 47% in large-scale data extraction operations, particularly in network-bound tasks. This performance advantage is crucial for applications that require rapid data collection, often utilising the fastest web scraping language from multiple sources.
- Concurrency: Go's goroutines enable developers to manage thousands of concurrent tasks with minimal overhead. This feature is especially beneficial for extracting large datasets from various sources simultaneously, allowing for efficient data collection without substantial resource use. Go can manage millions of simultaneous network connexions efficiently, further enhancing its capabilities in high-volume data extraction scenarios.
Use Cases:
- Large-Scale Scraping: Go excels in projects requiring the rapid scraping of vast amounts of data, such as price monitoring for e-commerce platforms or aggregating information from numerous APIs. Its ability to handle high-volume requests makes it a preferred choice for businesses needing timely insights. Additionally, Go has experienced a 12% rise in adoption specifically for backend and system programming tasks, including web extraction applications.
- Real-Time Data Processing: The language's performance capabilities make it ideal for applications that demand real-time data processing, such as monitoring social media trends or tracking stock prices. Go's efficiency allows for quick responses to changing data, enhancing decision-making processes.
In summary, Go stands out as the fastest web scraping language for programmers aiming to create high-performance web scrapers that can efficiently manage large-scale operations. With the global web data extraction market projected to exceed $2B by 2030, the significance of technologies like Go continues to expand.
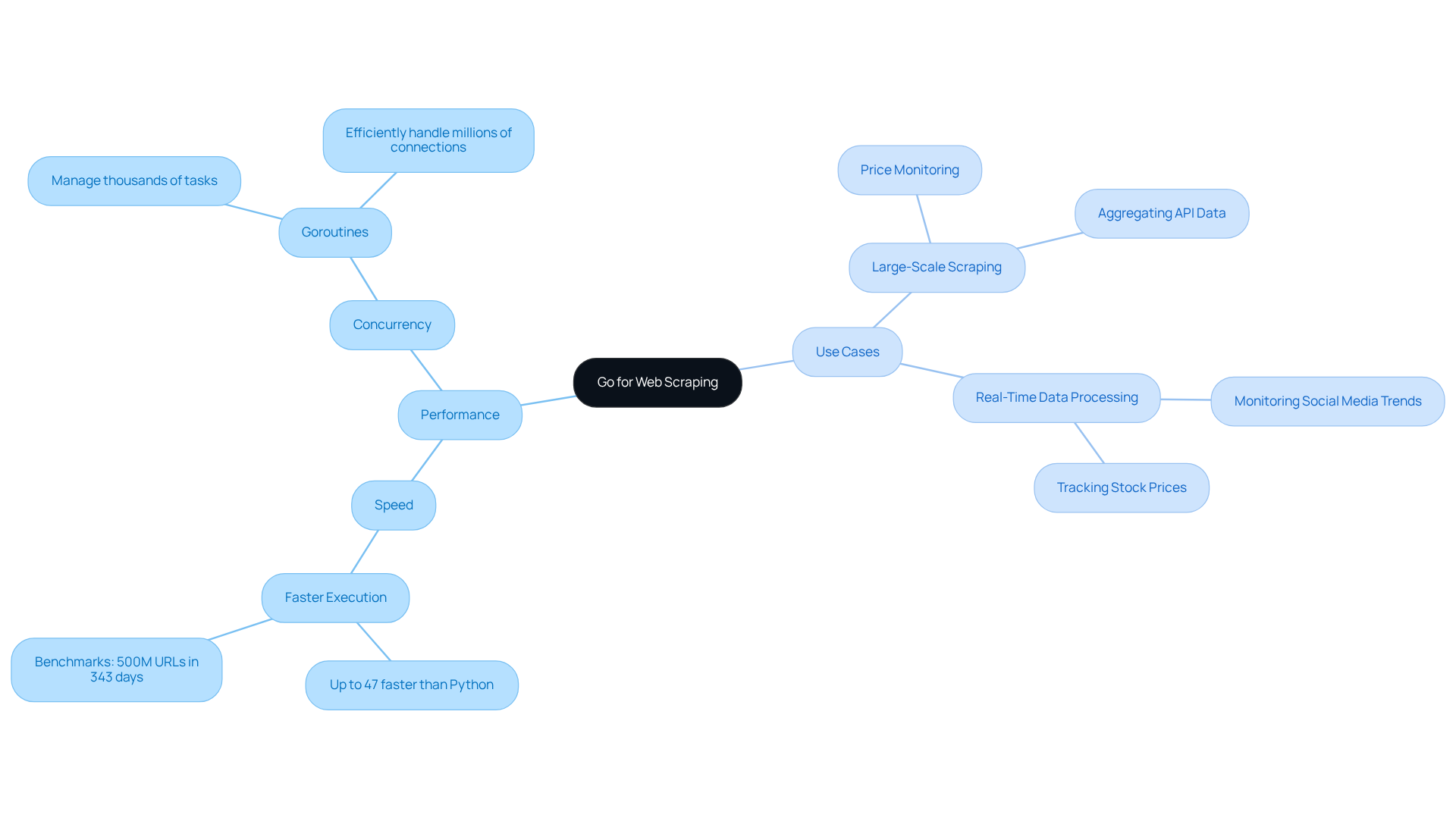
Exploring Rust: High-Performance Capabilities for Web Scraping
Rust has emerged as a compelling choice for web data extraction, especially as the fastest web scraping language for programmers seeking high performance and safety.
High Performance:
- Speed: Rust's compiled nature enables it to execute tasks at speeds comparable to C and C++, making it ideal for performance-critical applications. This efficiency is particularly beneficial in high-volume data extraction scenarios, where the fastest web scraping language is essential for minimising latency. Appstractor enhances this capability with its Rotating Proxy Servers, which can be operational within 24 hours, allowing programmers to quickly scale their data extraction efforts without delays.
- Memory Safety: Rust's ownership model guarantees memory safety without relying on a garbage collector, significantly lowering the risk of memory leaks and segmentation faults. This feature is vital for long-running data extraction tasks, where stability and reliability are crucial. Appstractor's Full Service option provides complete data delivery in formats such as JSON, CSV, and Parquet, further supporting developers in maintaining robust extraction solutions.
Use Cases:
- Complex Data Extraction: Rust excels in scraping intricate websites that employ advanced parsing techniques, particularly those built on JavaScript frameworks. Its capability to effectively manage dynamic content positions it as a strong contender for the title of fastest web scraping language in the web data extraction arena. With Appstractor's advanced data mining solutions, programmers can automate the extraction process, utilising flexible proxy options for seamless integration.
- Resource-Intensive Applications: For applications requiring high throughput and low latency, such as real-time data aggregation or processing large datasets, Rust delivers the necessary performance and reliability. Its memory safety features further enhance its suitability for these tasks, ensuring that programmers can develop resilient extraction solutions without compromising speed. Appstractor's Hybrid option allows businesses to broaden their data extraction initiatives while benefiting from expert support and transparent billing structures, with proxies charged per GB and no hidden overages.
As the web data collection market continues to evolve, projected to reach USD 2 billion by 2030, Rust's unique blend of speed and safety positions it as the fastest web scraping language, making it an attractive option for developers focused on creating efficient and resilient web extractors. Additionally, with 10.2% of all global web traffic now originating from scrapers, the importance of effective web data extraction technologies like Rust, complemented by Appstractor's innovative services, cannot be overstated.
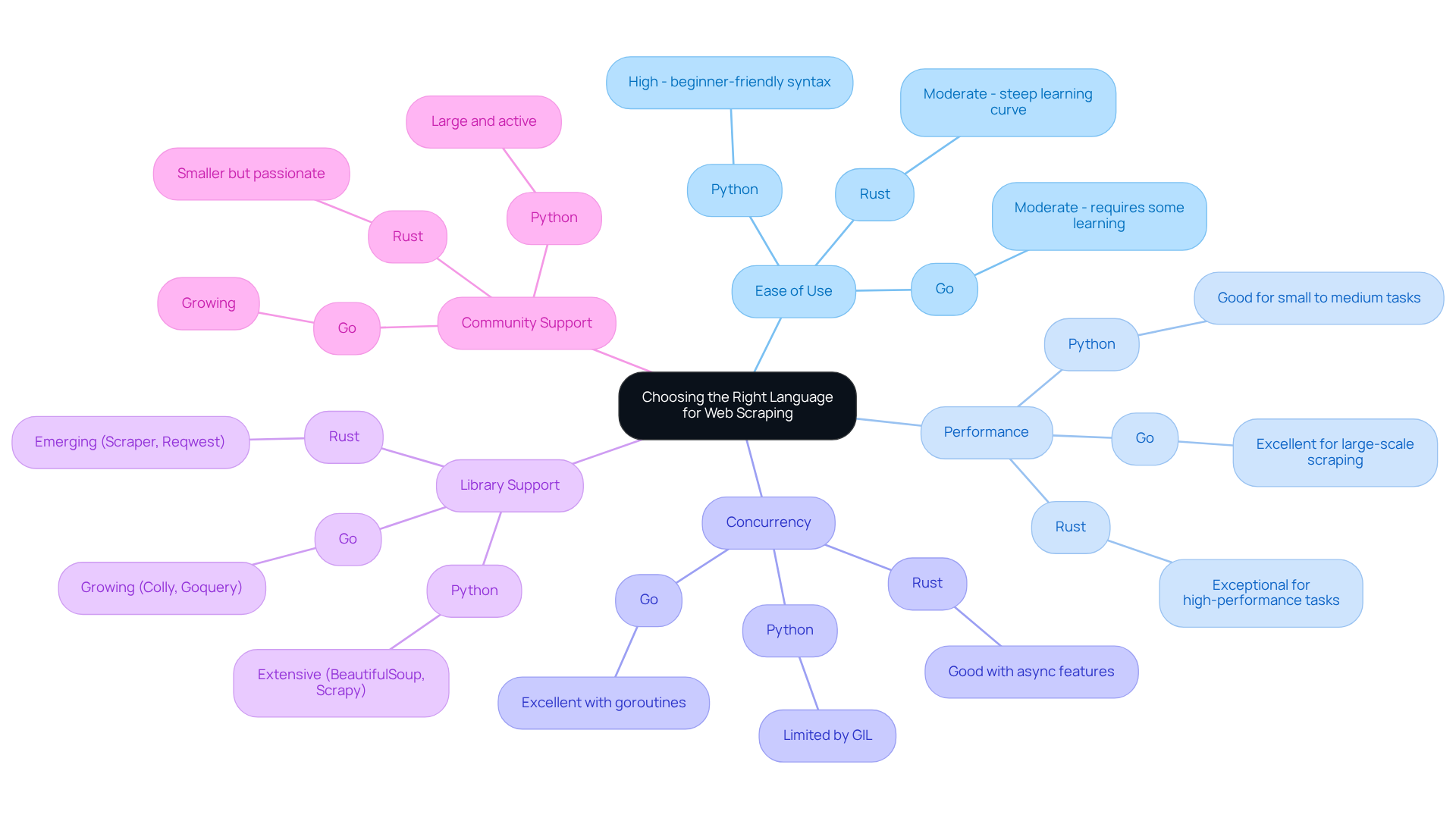
Comparative Summary: Choosing the Right Language for Your Web Scraping Needs
When selecting a programming language for web data extraction, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Below is a comparative summary of Python, Go, and Rust:
- Feature:
- Ease of Use:
- Python: High - beginner-friendly syntax
- Go: Moderate - requires some learning
- Rust: Moderate - steep learning curve
- Performance:
- Python: Good for small to medium tasks
- Go: Excellent for large-scale scraping
- Rust: Exceptional for high-performance tasks
- Concurrency:
- Python: Limited by GIL
- Go: Excellent with goroutines
- Rust: Good with async features
- Library Support:
- Python: Extensive (BeautifulSoup, Scrapy)
- Go: Growing (Colly, Goquery)
- Rust: Emerging (Scraper, Reqwest)
- Community Support:
- Python: Large and active
- Go: Growing
- Rust: Smaller but passionate
- Ease of Use:
In conclusion, Python is ideal for beginners and smaller projects. Go excels in performance and concurrency for large-scale scraping, while Rust is recognised as the fastest web scraping language, offering unmatched speed and safety for resource-intensive applications. The choice ultimately depends on the specific needs and constraints of your web scraping project.
Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the optimal language for web scraping is crucial for effective data extraction. This article has examined three leading options - Python, Go, and Rust - each with distinct strengths and challenges.
- Python is favoured for its user-friendly syntax and extensive library ecosystem, making it an excellent choice for beginners and small to medium projects.
- Go excels in performance and concurrency, establishing itself as the fastest web scraping language for large-scale operations.
- Rust offers high performance and memory safety, making it suitable for resource-intensive applications, particularly those requiring rapid data processing.
The discussion emphasised Python's ease of use and strong community support, which are significant advantages for developers embarking on their web scraping journey. Go's superior execution speed and concurrency capabilities render it highly effective for projects that necessitate swift data collection from multiple sources. Meanwhile, Rust's blend of speed and reliability is increasingly acknowledged, especially for complex scraping tasks that involve managing dynamic content.
Ultimately, the choice of web scraping language should align with specific project requirements, including the scale of data extraction, performance needs, and developer expertise. As the landscape of web data extraction evolves, understanding the strengths and limitations of each language is essential for making informed decisions. By embracing the right tools, businesses can significantly enhance the efficiency of their web scraping initiatives, enabling them to extract valuable insights from the vast amounts of data available online.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is web scraping?
Web scraping is a technique used to extract data from websites.
Which languages are considered the leading options for web scraping?
The three leading languages for web scraping are Python, Go, and Rust.
Why is Python often regarded as the fastest web scraping language?
Python is considered the fastest web scraping language due to its ease of use, robust libraries, extensive community support, and a high adoption rate among developers.
What are the advantages of using Python for web scraping?
Python offers clarity and simplicity, a strong collection of libraries like BeautifulSoup and Scrapy, extensive community resources, and a leading adoption rate of 69.6% among developers.
What are the key features of Go in web scraping?
Go is recognised for its performance and concurrency capabilities, making it suitable for large-scale data extraction operations, with a lightweight architecture that enhances its performance in high-demand applications.
What benefits does Rust provide for web scraping?
Rust combines high performance with memory safety, preventing common programming errors through strict compile-time checks, making it ideal for developing robust extraction tools.
What are the limitations of using Python for web scraping?
Python may struggle with performance in high-demand scenarios, particularly with large data volumes, due to its interpreted nature and the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL) that restricts concurrent thread execution.
How does the choice of a web scraping language depend on project requirements?
The choice between Go and Rust will depend on specific project needs, team expertise, and the desired balance between speed, reliability, and ease of use.
Is Python suitable for beginners in web scraping?
Yes, Python's straightforward syntax and extensive library ecosystem make it highly accessible for beginners looking to implement data extraction solutions.
List of Sources
- Understanding Web Scraping Languages: An Overview
- Web Scraping Report 2025: Market Trends, Growth & Key Insights (https://promptcloud.com/blog/state-of-web-scraping-2025-report)
- Best Language for Web Scraping (https://scrapingbee.com/blog/best-language-for-web-scraping)
- State of web scraping report 2025 (https://blog.apify.com/state-of-web-scraping)
- 50 Developer Quotes That Will Transform Your Coding Mindset (https://deliberatedirections.com/web-development-quotes-coding-design)
- Web Scraping Statistics & Trends You Need to Know in 2025 (https://scrapingdog.com/blog/web-scraping-statistics-and-trends)
- Evaluating Python: Strengths and Limitations in Web Scraping
- Case Studies & Projects (https://antrixacademy.com/AboutUs/case_studies.html)
- Web Scraping Report 2025: Market Trends, Growth & Key Insights (https://promptcloud.com/blog/state-of-web-scraping-2025-report)
- Web Scraping Market Report 2025 | ScrapeOps (https://scrapeops.io/web-scraping-playbook/web-scraping-market-report-2025)
- The State of Web Crawling in 2025: Key Statistics and Industry Benchmarks (https://thunderbit.com/blog/web-crawling-stats-and-industry-benchmarks)
- Assessing Go: Performance and Use Cases for Web Scraping
- Go vs Python for Web Scraping: The Ultimate Performance-Focused Guide (2025) / litport.net (https://litport.net/blog/go-vs-python-for-web-scraping-the-ultimate-performance-focused-guide-47279)
- Web Scraping Report 2025: Market Trends, Growth & Key Insights (https://promptcloud.com/blog/state-of-web-scraping-2025-report)
- None (https://capsolver.com/blog/web-scraping/best-coding-language-for-web-scraping)
- The Best Language for Web Scraping: Python’s Simplicity vs. Go’s Speed - IPFLY (https://ipfly.net/blog/python-vs-go-web-scraping)
- Exploring Rust: High-Performance Capabilities for Web Scraping
- Best Language for Web Scraping (https://scrapingbee.com/blog/best-language-for-web-scraping)
- Rust Web Scraping in 2026 - ZenRows (https://zenrows.com/blog/rust-web-scraping)
- Web Scraping Report 2025: Market Trends, Growth & Key Insights (https://promptcloud.com/blog/state-of-web-scraping-2025-report)
- only_scraper - Rust (https://docs.rs/only_scraper)
- None (https://capsolver.com/blog/web-scraping/best-coding-language-for-web-scraping)
- Comparative Summary: Choosing the Right Language for Your Web Scraping Needs
- Best Language for Web Scraping (https://scrapingbee.com/blog/best-language-for-web-scraping)




